Close association of aquaporin-2 internalization with caveolin-1
- PMID: 22685356
- PMCID: PMC3365305
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.12003
Close association of aquaporin-2 internalization with caveolin-1
Abstract
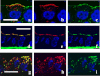
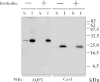
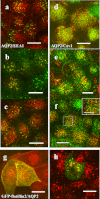
Aquaporin 2 (AQP2) is a membrane water channel protein that traffics between the intracellular membrane compartment and the plasma membrane in a vasopressin-dependent manner in the renal collecting duct cell to control the amount of water reabsorption. We examined the relation between AQP2 internalization from the plasma membrane and caveolin-1, which is a major protein in membrane microdomain caveolae, in Mardin-Darby canine kidney cells expressing human AQP2 (MDCK-hAQP2 cells). Double-immunofluorescence microscopy showed that AQP2 is colocalized with caveolin-1 in the apical plasma membrane by stimulating the intracellular signaling cascade of vasopressin with forskolin. After washing forskolin, both AQP2 and caveolin-1 were internalized to early endosomes and then separately went back to their individual compartments, which are subapical compartments and the apical membrane, respectively.Double-immunogold electron microscopy in ultrathin cryosections confirmed the colocalization of AQP2 with caveolin-1 at caveolar structures on the apical plasma membrane of forskolin-treated cells and the colocalization within the same intracellular vesicles after washing forskolin. A co-immunoprecipitation experiment showed the close interaction between AQP2 and caveolin-1 in forskolin-treated cells and in cells after washing forskolin. These results suggest that a caveolin-1-dependent and possibly caveolar-dependent pathway is a candidate for AQP2 internalization in MDCK cells.
Keywords: MDCK cells; apical membrane; aquaporin-2; caveolin-1; early endosome.
Figures




References
-
- Aoki T., Nomura R., Fujimoto T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 in the endothelium. Exp. Cell Res. 1999;253:629–636. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T., Hagiwara H., Matsuzaki T., Suzuki T., Takata K. Internalization of caveolae and their relationship with endosomes in cultured human and mouse endothelial cells. Anat. Sci. Int. 2007;82:82–97. - PubMed
-
- Asai T., Kuwahara M., Kurihara H., Sakai T., Terada Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Pathogenesis of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by aquaporin-2 C-terminus mutations. Kidney Int. 2003;64:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Brown D. The ins and outs of aquaporin-2 trafficking. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2003;284:F893–F901. - PubMed

