Hybrid dispersion laser scanner
- PMID: 22685627
- PMCID: PMC3370333
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00445
Hybrid dispersion laser scanner
Abstract
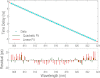
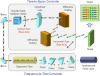
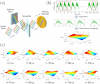
Laser scanning technology is one of the most integral parts of today's scientific research, manufacturing, defense, and biomedicine. In many applications, high-speed scanning capability is essential for scanning a large area in a short time and multi-dimensional sensing of moving objects and dynamical processes with fine temporal resolution. Unfortunately, conventional laser scanners are often too slow, resulting in limited precision and utility. Here we present a new type of laser scanner that offers ∼1,000 times higher scan rates than conventional state-of-the-art scanners. This method employs spatial dispersion of temporally stretched broadband optical pulses onto the target, enabling inertia-free laser scans at unprecedented scan rates of nearly 100 MHz at 800 nm. To show our scanner's broad utility, we use it to demonstrate unique and previously difficult-to-achieve capabilities in imaging, surface vibrometry, and flow cytometry at a record 2D raster scan rate of more than 100 kHz with 27,000 resolvable points.
Figures

References
-
- Marshall G. F. Handbook of optical and laser scanning (Dekker, New York, 2009).
-
- Fujii T. & Fukuchi T. Laser remote sensing (CRC Press, New York, 2005).
-
- Dotson C. L. Fundamentals of dimensional metrology (Delmar Cengage Learning, New York, 2006).
-
- Popescu G., Ikeda T., Goda K., Best-Popescu C. A., Laposata M. L., Manley S., Dasari R. R., Badizadegan K. & Feld M. S. Optical measurement of cell membrane tension. Physical Review Letters 97, 218101 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Gobel W., Kampa B. M. & Helmchen F. Imaging cellular network dynamics in three dimensions using fast 3D laser scanning. Nature Methods 4, 73–79 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

