Delayed apoptosis by neutrophils from COPD patients is associated with altered Bak, Bcl-xl, and Mcl-1 mRNA expression
- PMID: 22686245
- PMCID: PMC3488503
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-65
Delayed apoptosis by neutrophils from COPD patients is associated with altered Bak, Bcl-xl, and Mcl-1 mRNA expression
Abstract
Background: Delayed neutrophil apoptosis may be an important factor in the persistent inflammation associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Bcl-2 family proteins are important regulators of neutrophil apoptosis. We determined the mRNA levels of pro-apoptotic Bak and anti-aptototic Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 members of the Bcl-2 family in unstimulated peripheral blood neutrophils from patients with mild to moderate COPD and compared these to neutrophils from healthy controls.
Methods: Neutrophils were isolated from peripheral blood samples of 47 COPD patients (smokers: N = 24) and 47 healthy controls (smokers: N = 24). Percentages of apoptotic cells were determined at 4, 24, and 36 h for unstimulated neutrophils cultured in vitro. Neutrophil mRNA expression of Bak, Bcl-xl, and Mcl-1 was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). FEV1 (% predicted) and FVC were determined by spirometry and correlations between mRNA levels and lung function parameters were determined.
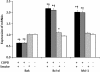
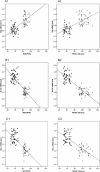
Results: The percentages of apoptotic cells among unstimulated neutrophils from COPD patients were significantly lower compared to cells from controls after 4, 24, and 36 h in culture; smoking history had only a minimal effect on these differences. Unstimulated neutrophils from COPD patients had significantly lower Bak mRNA expression and higher expressions of Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 mRNA than cells from healthy controls. Again, smoking history had only a minimal effect on these trends. Bak mRNA expression was significantly positively correlated with both % predicted FEV1 and the FEV1/FVC ratio, while Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 mRNA expressions were significantly negatively correlated with %predicted FEV1 and the FEV1/FVC ratio.
Conclusions: The genes for pro-apoptotic Bak, and anti-apoptotic Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 may be important in regulating the delayed neutrophil apoptosis observed in COPD, which may contribute to COPD pathogenesis.
Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/1605269445677066.
Figures
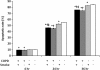
References
-
- Colby J, Goldman M. Update on the management of COPD. Conn Med. 2009;73:217–221. - PubMed
-
- Haslett C. Granulocyte apoptosis and its role in the resolution and control of lung inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:S5–S11. - PubMed
-
- Saetta M. Airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:S17–S20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

