Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances
- PMID: 22686334
- PMCID: PMC6493516
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00340.x
Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances
Abstract
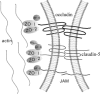
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a dynamic interference that regulates the nutrition and toxic substance in and out of the central nervous system (CNS), and plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable circumstance of the CNS. Tight junctions among adjacent cells form the basic structure of BBB to limiting paracellular permeability. In the present review, the constituents of tight junction proteins are depicted in detail, together with the regulation of tight junction under stimulation and in pathological conditions. Tight junction modulators are also discussed.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cardoso FL, Brites D, Brito MA. Looking at the blood‐brain barrier: Molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res Rev 2010;64:328–363. - PubMed
-
- Tam SJ, Watts RJ. Connecting vascular and nervous system development: Angiogenesis and the blood‐brain barrier. Annu Rev Neurosci 2010;33:379–408. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood‐brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 2005;57:173–185. - PubMed
-
- Pardridge WM. Blood‐brain barrier delivery. Drug Discov Today 2007;12:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Neuwelt EA. Mechanisms of disease: The blood‐brain barrier. Neurosurgery 2004;54:131–140; discussion 141–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources