Tests of a direct effect of childhood abuse on adult borderline personality disorder traits: a longitudinal discordant twin design
- PMID: 22686871
- PMCID: PMC3482426
- DOI: 10.1037/a0028328
Tests of a direct effect of childhood abuse on adult borderline personality disorder traits: a longitudinal discordant twin design
Abstract
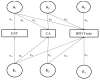
We used a longitudinal twin design to examine the causal association between sexual, emotional, and physical abuse in childhood (before age 18) and borderline personality disorder (BPD) traits at age 24 using a discordant twin design and biometric modeling. Additionally, we examined the mediating and moderating effects of symptoms of childhood externalizing and internalizing disorders on the link between childhood abuse and BPD traits. Although childhood abuse, BPD traits, and internalizing and externalizing symptoms were all correlated, the discordant twin analyses and biometric modeling showed little to no evidence that was consistent with a causal effect of childhood abuse on BPD traits. Instead, our results indicate that the association between childhood abuse and BPD traits stems from common genetic influences that, in some cases, also overlap with internalizing and externalizing disorders. These findings are inconsistent with the widely held assumption that childhood abuse causes BPD, and they suggest that BPD traits in adulthood are better accounted for by heritable vulnerabilities to internalizing and externalizing disorders.
2013 APA, all rights reserved
Figures
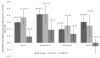
Similar articles
-
Childhood trauma and borderline personality disorder traits: A discordant twin study.J Psychopathol Clin Sci. 2022 May;131(4):365-374. doi: 10.1037/abn0000755. Epub 2022 Apr 4. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. 2022. PMID: 35377676
-
Stability, change, and heritability of borderline personality disorder traits from adolescence to adulthood: a longitudinal twin study.Dev Psychopathol. 2009 Fall;21(4):1335-53. doi: 10.1017/S0954579409990186. Dev Psychopathol. 2009. PMID: 19825271 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal twin study of borderline personality disorder traits and substance use in adolescence: developmental change, reciprocal effects, and genetic and environmental influences.Personal Disord. 2013 Jan;4(1):23-32. doi: 10.1037/a0027178. Epub 2012 May 28. Personal Disord. 2013. PMID: 22642461 Free PMC article.
-
The link between rejection sensitivity and borderline personality disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Clin Psychol. 2019 Sep;58(3):289-326. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12216. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Br J Clin Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30900278
-
[The main directions of research on the causes conditioning the occurrence of the borderline personality disorders].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2011 Oct;31(184):252-5. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2011. PMID: 22097186 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Trait-based assessment of borderline personality disorder using the NEO Five-Factor Inventory: Phenotypic and genetic support.Psychol Assess. 2016 Jan;28(1):39-50. doi: 10.1037/pas0000142. Epub 2015 May 18. Psychol Assess. 2016. PMID: 25984635 Free PMC article.
-
Early Detection and Outcome in Borderline Personality Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Oct 9;10:710. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00710. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31649564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Borderline Personality Disorder: Risk Factors and Early Detection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;11(11):2142. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11112142. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of genetic and environmental risk factors for symptoms of DSM-IV borderline personality disorder.JAMA Psychiatry. 2013 Nov;70(11):1206-14. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1944. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24048243 Free PMC article.
-
Dialectical Behavior Therapy for Adolescents with Borderline Personality Disorder: Emotion Dysregulation, Abuse, and Treatment Outcomes.Evid Based Pract Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2025;10(1):33-45. doi: 10.1080/23794925.2024.2306625. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Evid Based Pract Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40406511
References
-
- Achenbach TM, McConaughy SH, Howell CT. Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: implications of cross-informant correlations. Psychological Bulletin. 1987;101(2):213–232. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR. Washington, DC: 2000.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed) Washington, DC: 1994.
-
- Arens EA, Grabe HJ, Spitzer C, Barnow S. Testing the biosocial model of borderline personality disorder: Results of a prospective 5-year longitudinal study. Personality and Mental Health. 2011;5(1):29–42.
-
- Ayers W, Haslam N, Bernstein DP, Tryon WT, Handelsman L. Categorical vs Dimensional models of personality disorders in substance abusers: A taxometric analysis; Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association.1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

