Supplemental choline during the periweaning period protects against trace conditioning impairments attributable to post-training ethanol exposure in adolescent rats
- PMID: 22687150
- PMCID: PMC3409289
- DOI: 10.1037/a0028878
Supplemental choline during the periweaning period protects against trace conditioning impairments attributable to post-training ethanol exposure in adolescent rats
Abstract
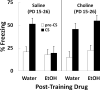
Supplemental choline during early stages of development can result in long-lasting improvements to memory function. In addition, pre- or postnatal choline has been shown to be protective against some of the adverse effects of early alcohol exposure. The present experiment examined whether supplemental choline given to rats would protect against the effects of posttraining alcohol administration on trace fear conditioning. Posttraining alcohol exposure in adolescent rats results in poor performance in this hippocampus-dependent task, although delay conditioning is unaffected. Here, rats were given an s.c. injection of either saline or choline chloride daily on postnatal days (PD) 15-26. On PD 30 subjects were trained in a trace fear conditioning procedure. For the next 3 days animals were administered 2.5 g/kg ethanol or water control, and conditional stimulus (CS)-elicited freezing was measured on PD 34. Results indicated that posttraining alcohol disrupted the expression of trace conditioning and that supplemental choline on PD 15-26 was protective against this effect. That is, choline-treated animals subsequently given posttraining ethanol performed as well as animals not given ethanol. These results indicate that supplemental choline given during the periweaning period protects against ethanol-induced impairments in a hippocampus-dependent learning task. Findings contribute to the growing literature showing improvements in learning and memory in subjects given extra dietary choline during critical periods of brain development.
Figures
References
-
- Abreu-Villaca Y, Filgueiras CC, Manhaes AC. Developmental aspects of the cholinergic system. Behavioural Brain Research. 2011;221:367–378. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer S. Postnatal development of the hippocampal dentate gyrus under normal and experimental conditions. In: Isaacson RL, Pribram KH, editors. The hippocampus: structure and development. Vol. 1. Plenum; New York: 1975. pp. 95–122.
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Maren S, Sage JR, Goodrich S, Fanselow MS. Scopolamine and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: Dose-effect analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:731–744. - PubMed
-
- Barnet RC, Hunt PS. Trace and long-delay fear conditioning in the developing rat. Learning and Behavior. 2005;33:437–443. - PubMed
-
- Bonthius DJ, West JR. Alcohol-induced neuronal loss in developing rats: Increased brain damage with binge exposure. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1990;14:107–118. - PubMed

