Understanding the molecular determinants of substrate and inhibitor specificities in the Carbapenemase KPC-2: exploring the roles of Arg220 and Glu276
- PMID: 22687511
- PMCID: PMC3421566
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05769-11
Understanding the molecular determinants of substrate and inhibitor specificities in the Carbapenemase KPC-2: exploring the roles of Arg220 and Glu276
Abstract
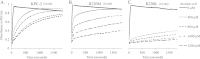
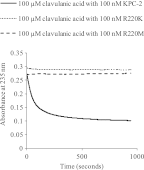
β-Lactamases are important antibiotic resistance determinants expressed by bacteria. By studying the mechanistic properties of β-lactamases, we can identify opportunities to circumvent resistance through the design of novel inhibitors. Comparative amino acid sequence analysis of class A β-lactamases reveals that many enzymes possess a localized positively charged residue (e.g., R220, R244, or R276) that is critical for interactions with β-lactams and β-lactamase inhibitors. To better understand the contribution of these residues to the catalytic process, we explored the roles of R220 and E276 in KPC-2, a class A β-lactamase that inactivates carbapenems and β-lactamase inhibitors. Our study reveals that substitutions at R220 of KPC-2 selectively impact catalytic activity toward substrates (50% or greater reduction in k(cat)/K(m)). In addition, we find that residue 220 is central to the mechanism of β-lactamase inhibition/inactivation. Among the variants tested at Ambler position 220, the R220K enzyme is relatively "inhibitor susceptible" (K(i) of 14 ± 1 μM for clavulanic acid versus K(i) of 25 ± 2 μM for KPC-2). Specifically, the R220K enzyme is impaired in its ability to hydrolyze clavulanic acid compared to KPC-2. In contrast, the R220M substitution enzyme demonstrates increased K(m) values for β-lactamase inhibitors (>100 μM for clavulanic acid versus 25 ± 3 μM for the wild type [WT]), which results in inhibitor resistance. Unlike other class A β-lactamases (i.e., SHV-1 and TEM-1), the amino acid present at residue 276 plays a structural rather than kinetic role with substrates or inhibitors. To rationalize these findings, we constructed molecular models of clavulanic acid docked into the active sites of KPC-2 and the "relatively" clavulanic acid-susceptible R220K variant. These models suggest that a major 3.5-Å shift occurs of residue E276 in the R220K variant toward the active S70 site. We anticipate that this shift alters the shape of the active site and the positions of two key water molecules. Modeling also suggests that residue 276 may assist with the positioning of the substrate and inhibitor in the active site. These biochemical and molecular modeling insights bring us one step closer to understanding important structure-activity relationships that define the catalytic and inhibitor-resistant profile of KPC-2 and can assist the design of novel compounds.
Figures

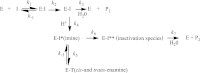
Similar articles
-
Variants of β-lactamase KPC-2 that are resistant to inhibition by avibactam.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jul;59(7):3710-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04406-14. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25666153 Free PMC article.
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-2 (KPC-2), Substitutions at Ambler Position Asp179, and Resistance to Ceftazidime-Avibactam: Unique Antibiotic-Resistant Phenotypes Emerge from β-Lactamase Protein Engineering.mBio. 2017 Oct 31;8(5):e00528-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00528-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29089425 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate selectivity and a novel role in inhibitor discrimination by residue 237 in the KPC-2 beta-lactamase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jul;54(7):2867-77. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00197-10. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20421396 Free PMC article.
-
β-Lactamases and β-Lactamase Inhibitors in the 21st Century.J Mol Biol. 2019 Aug 23;431(18):3472-3500. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30959050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SHV-type beta-lactamases.Curr Pharm Des. 1999 Nov;5(11):847-64. Curr Pharm Des. 1999. PMID: 10539992 Review.
Cited by
-
Variants of β-lactamase KPC-2 that are resistant to inhibition by avibactam.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jul;59(7):3710-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04406-14. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25666153 Free PMC article.
-
Succession and persistence of microbial communities and antimicrobial resistance genes associated with International Space Station environmental surfaces.Microbiome. 2018 Nov 13;6(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0585-2. Microbiome. 2018. PMID: 30424821 Free PMC article.
-
A Structure-Based Classification of Class A β-Lactamases, a Broadly Diverse Family of Enzymes.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Jan;29(1):29-57. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00019-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26511485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different Conformations Revealed by NMR Underlie Resistance to Ceftazidime/Avibactam and Susceptibility to Meropenem and Imipenem among D179Y Variants of KPC β-Lactamase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Apr 19;66(4):e0212421. doi: 10.1128/aac.02124-21. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35311523 Free PMC article.
-
Nacubactam Enhances Meropenem Activity against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Producing KPC.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jul 25;63(8):e00432-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00432-19. Print 2019 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31182530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambler RP. 1980. The structure of β-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 289:321–331 - PubMed
-
- Brown RP, Aplin RT, Schofield CJ. 1996. Inhibition of TEM-2 β-lactamase from Escherichia coli by clavulanic acid: observation of intermediates by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 35:12421–12432 - PubMed
-
- Carmeli Y, et al. 2010. Controlling the spread of carbapenemase-producing Gram-negatives: therapeutic approach and infection control. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 16:102–111 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2008. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard —1st ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

