Effects of chronic heart failure on neuronal nitric oxide synthase-mediated control of microvascular O2 pressure in contracting rat skeletal muscle
- PMID: 22687613
- PMCID: PMC3547272
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.235929
Effects of chronic heart failure on neuronal nitric oxide synthase-mediated control of microvascular O2 pressure in contracting rat skeletal muscle
Abstract
Chronic heart failure (CHF) impairs nitric oxide (NO)-mediated regulation of the skeletal muscle microvascular O(2) delivery/V(O(2)) ratio (which sets the microvascular O(2) pressure, PO(2)mv). Given the pervasiveness of endothelial dysfunction in CHF, this NO-mediated dysregulation is attributed generally to eNOS. It is unknown whether nNOS-mediated PO(2)mv regulation is altered in CHF. We tested the hypothesis that CHF impairs nNOS-mediated PO(2)mv control. In healthy and CHF (left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP): 6 ± 1 versus 14 ± 1 mmHg, respectively, P < 0.05) rats spinotrapezius muscle blood flow (radiolabelled microspheres), PO(2)mv (phosphorescence quenching), and V(O(2)) (Fick calculation) were measured before and after 0.56 mg kg(-1)i.a. of the selective nNOS inhibitor S-methyl-l-thiocitrulline (SMTC). In healthy rats, SMTC increased baseline PO(2)mv (
Control: 29.7 ± 1.4, SMTC: 34.4 ± 1.9 mmHg, P < 0.05) by reducing V(O(2)) (↓20%) without any effect on blood flow and speeded the mean response time (MRT, time to reach 63% of the overall kinetics response,
Control: 24.2 ± 2.0, SMTC: 18.5 ± 1.3 s, P < 0.05). In CHF rats, SMTC did not alter baseline PO(2)mv (
Control: 25.7 ± 1.6, SMTC: 28.6 ± 2.1 mmHg, P > 0.05), V(O(2)) at rest, or the MRT (CONTROL: 22.8 ± 2.6, SMTC: 21.3 ± 3.0 s, P > 0.05). During the contracting steady-state, SMTC reduced blood flow (↓15%) and V(O(2)) (↓15%) in healthy rats such that PO(2)mv was unaltered (
Control: 19.8 ± 1.7, SMTC: 20.7 ± 1.8 mmHg, P > 0.05). In marked contrast, in CHF rats SMTC did not change contracting steady-state blood flow, V(O(2)), or PO(2)mv (
Control: 17.0 ± 1.4, SMTC: 17.7 ± 1.8 mmHg, P > 0.05). nNOS-mediated control of skeletal muscle microvascular function is compromised in CHF versus healthy rats. Treatments designed to ameliorate microvascular dysfunction in CHF may benefit by targeting improvements in nNOS function.
Figures
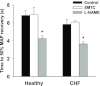
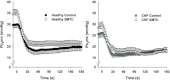
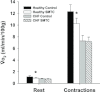
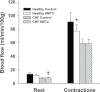
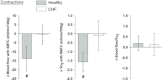
 in healthy (n = 14) or CHF (n = 12) rats; but these values were achieved very differently (i.e. blood flow and
in healthy (n = 14) or CHF (n = 12) rats; but these values were achieved very differently (i.e. blood flow and  reductions in healthy rats compared to no changes in CHF rats). Data are means ± SEM. #P < 0.05 versus zero.
reductions in healthy rats compared to no changes in CHF rats). Data are means ± SEM. #P < 0.05 versus zero.Similar articles
-
Role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in modulating microvascular and contractile function in rat skeletal muscle.Microcirculation. 2011 Aug;18(6):501-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2011.00111.x. Microcirculation. 2011. PMID: 21535296
-
Effects of neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition on microvascular and contractile function in skeletal muscle of aged rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):H1076-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00477.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22923618 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive chronic heart failure slows the recovery of microvascular O2 pressures after contractions in the rat spinotrapezius muscle.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):H1755-61. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00590.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20817826 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition on resting and exercising hindlimb muscle blood flow in the rat.J Physiol. 2010 Apr 15;588(Pt 8):1321-31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.183723. Epub 2010 Feb 22. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20176629 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle microvascular oxygenation dynamics in heart failure: exercise training and nitric oxide-mediated function.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Mar 1;306(5):H690-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00901.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24414070 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition and regional sympathetic nerve discharge: implications for peripheral vascular control.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013 May 1;186(3):285-9. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2013.02.021. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23454026 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of sodium nitrite on local control of contracting skeletal muscle microvascular oxygen pressure in healthy rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Jan 1;122(1):153-160. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00367.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 27. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 27789769 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Power: An Important Fatigue Threshold in Exercise Physiology.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016 Nov;48(11):2320-2334. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000939. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016. PMID: 27031742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edward F. Adolph Distinguished Lecture. Contemporary model of muscle microcirculation: gateway to function and dysfunction.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Oct 1;127(4):1012-1033. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00013.2019. Epub 2019 May 16. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 31095460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise training in chronic heart failure: improving skeletal muscle O2 transport and utilization.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Nov;309(9):H1419-39. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00469.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26320036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman P, Dittmer D. Biological Data Book. 2nd edn. Bethesda, MD: FASEB; 1974.
-
- Bailey JK, Kindig CA, Behnke BJ, Musch TI, Schmid-Schoenbein GW, Poole DC. Spinotrapezius muscle microcirculatory function: effects of surgical exteriorization. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H3131–3137. - PubMed
-
- Baker DJ, Krause DJ, Howlett RA, Hepple RT. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition reduces O2 cost of force development and spares high-energy phosphates following contractions in pump-perfused rat hindlimb muscles. Exp Physiol. 2006;91:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Behnke BJ, Delp MD, McDonough P, Spier SA, Poole DC, Musch TI. Effects of chronic heart failure on microvascular oxygen exchange dynamics in muscles of contrasting fiber type. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61:325–332. - PubMed
-
- Bertaglia RS, Reissler J, Lopes FS, Cavalcante WL, Carani FR, Padovani CR, Rodrigues SA, Cigogna AC, Carvalho RF, Fernandes AA, Gallacci M, Silva MD. Differential morphofunctional characteristics and gene expression in fast and slow muscle of rats with monocrotaline-induced heart failure. J Mol Histol. 2011;42:205–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

