Fall in C-peptide during first 2 years from diagnosis: evidence of at least two distinct phases from composite Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet data
- PMID: 22688329
- PMCID: PMC3402330
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1538
Fall in C-peptide during first 2 years from diagnosis: evidence of at least two distinct phases from composite Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet data
Abstract
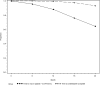
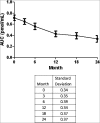
Interpretation of clinical trials to alter the decline in β-cell function after diagnosis of type 1 diabetes depends on a robust understanding of the natural history of disease. Combining data from the Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet studies, we describe the natural history of β-cell function from shortly after diagnosis through 2 years post study randomization, assess the degree of variability between patients, and investigate factors that may be related to C-peptide preservation or loss. We found that 93% of individuals have detectable C-peptide 2 years from diagnosis. In 11% of subjects, there was no significant fall from baseline by 2 years. There was a biphasic decline in C-peptide; the C-peptide slope was -0.0245 pmol/mL/month (95% CI -0.0271 to -0.0215) through the first 12 months and -0.0079 (-0.0113 to -0.0050) from 12 to 24 months (P < 0.001). This pattern of fall in C-peptide over time has implications for understanding trial results in which effects of therapy are most pronounced early and raises the possibility that there are time-dependent differences in pathophysiology. The robust data on the C-peptide obtained under clinical trial conditions should be used in planning and interpretation of clinical trials.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on: Greenbaum et al. Fall in C-peptide during first 2 years from diagnosis: evidence of at least two distinct phases from composite type 1 Diabetes TrialNet data. Diabetes 2012;61:2066-2073.Diabetes. 2013 Jun;62(6):e7. doi: 10.2337/db13-0047. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23704534 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to Comment on: Greenbaum et al. Fall in C-peptide during first 2 years from diagnosis: evidence of at least two distinct phases from composite type 1 diabetes TrialNet data. Diabetes 2012;61:2066-2073.Diabetes. 2013 Jun;62(6):e8. doi: 10.2337/db13-0115. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23704535 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hermann R, Knip M, Veijola R, et al. FinnDiane Study Group . Temporal changes in the frequencies of HLA genotypes in patients with type 1 diabetes—indication of an increased environmental pressure? Diabetologia 2003;46:420–425 - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll M. Prevalence of overweight, obesity, and extreme obesity among adults: United States, trends 1960–1962 through 2007–2008 [article online], 2010. Available from www.cdc.gov/NCHS/data/hestat/obesity_adult_07_08/obesity_adult_07_08.pdf. Accessed 25 June 2011
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll M. Prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents: United States, trends 1963–1965 through 2007–2008 [article online], 2010. Available from www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/obesity_child_07_08/obesity_child_07_08.pdf. Accessed 25 June 2011
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-084565/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR024978/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024977/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001085/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800019C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-061016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000130/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical