The Cancer BioChip System: a functional genomic assay for anchorage-independent three-dimensional breast cancer cell growth
- PMID: 22689254
- PMCID: PMC3467330
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-012-0116-8
The Cancer BioChip System: a functional genomic assay for anchorage-independent three-dimensional breast cancer cell growth
Abstract
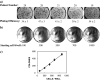
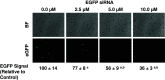
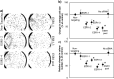
Advances in genomic research have revealed that each patient has their own unique tumor profile. While silencing RNA (siRNA) screening tests can identify which genes drive tumor cell growth, results obtained from these assays have been limited in their clinical translatability because they employ cell lines growing on flat surfaces. The Cancer BioChip System (CBCS) is a functional screening assay for identification of siRNA capable of inhibiting anchorage-independent three-dimensional (3D) cancer cell growth. Anchorage-independent growth assays are important in vitro predicators of regulators of cancer cell growth. Unique features of the CBCS include a Cancer BioChip, wherein cells incorporate different siRNAs in parallel and grow in a 3D matrix to form colonies that can be quantified using real-time imaging and an image analysis software. Thus, the CBCS can be developed as a tool for personalized identification of targeted cancer therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
R.A.A, J.N.M, and A.L.D are employed by Falcon Genomics, Inc. M.P.Z was a previous intern of Falcon Genomics, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Validation of the Cancer BioChip System as a 3D siRNA screening tool for breast cancer targets.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046086. Epub 2012 Sep 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049944 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of the c-Jun-N-terminal kinase expression by siRNA inhibits MCF-7 breast carcinoma cell line growth.Oncol Rep. 2010 Nov;24(5):1339-45. doi: 10.3892/or_00000991. Oncol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20878129
-
Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2544-52. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2203. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16510571
-
Down-regulation of hepatoma-derived growth factor inhibits anchorage-independent growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 1;66(1):18-23. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3905. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16397209
-
Inhibition effect of siRNA-downregulated UHRF1 on breast cancer growth.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2011 Apr;26(2):183-9. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2010.0886. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2011. PMID: 21539450
Cited by
-
Validation of the Cancer BioChip System as a 3D siRNA screening tool for breast cancer targets.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046086. Epub 2012 Sep 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049944 Free PMC article.
-
miR-125a inhibits the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells via suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2015 Aug;10(2):681-686. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3264. Epub 2015 May 26. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26622553 Free PMC article.
-
miR-196b regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2016 Mar;11(3):1745-1749. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4141. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26998071 Free PMC article.
-
miR-125a-5p-targeted regulation of TRA2β expression inhibits proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):14074-14080. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 35035750 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

