Effect of novel phosphoramidate on growth and respiratory metabolism of Paramecium aurelia
- PMID: 22690051
- PMCID: PMC3361778
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-9668.95949
Effect of novel phosphoramidate on growth and respiratory metabolism of Paramecium aurelia
Abstract
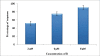
The continuous increase in the number of new chemicals as well as the discharges of solid and liquid wastes triggered the need for simple and inexpensive bioassays for routine testing. In recent years, there has been increasing development of methods (particularly rapid tests) for testing environmental samples. This paper describes the quick toxic evaluation of a novel synthetic compound: Phosphoramidate derivative B at different concentrations (2, 4 and 8 μM) for 72 h on Paramecium aurelia. We showed that B concentrations affect the growth of Paramecium in concentration- dependent manner; also it decreases the growth rate and increases response percentage in concentration- dependent manner. The value of LC50 obtained for these protozoa was estimated at 4.9693 μM after 24 hours of exposure. The respiratory metabolism of protozoan is perturbed at three concentrations, noting that the oxygen consumption was significantly increased at high concentrations after 18 hours of exposure. The results indicate that the Paramecium toxicity assay could be used as a complementary system to rapidly elucidate the cytotoxic potential of insecticides. The major advantages associated with these tests are: inexpensive, simple, rapid and seem to be attractive alternatives to conventional bioassays.
Keywords: Cytotoxic tests; Paramecium aurelia; growth kinetics; phosphoramidate B; respiratory metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Eto M. Organophosphorus Pesticides. Cleveland: Academic Press; 1974. Organic and Biological Chemistry. In: CRC Press Inc, editor.
-
- Zinkl JG, Shea PJ, Nakamoto RJ, Callman JE. Effects on cholinesterases of rainbow trout exposed to acephate and methamidophos. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1987;38:22–28. - PubMed
-
- Jena GB, Bhunya SP. Mutagenicity of an organophosphate insecticide acephate an in vivo study in chicks. Mutagenesis. 1994;9:319–324. - PubMed
-
- Carver H, Bootman J, Cimino MC, Esber HJ, Kirby P, Kirkhart B, et al. Genotoxic potential of acephate technical: in vitro and in vivo effects. Toxicology. 1985;35:125–42. - PubMed
-
- Perocco P, Del Ciello C, Colacci A, Pozzetti L, Paolini M, Cantelli-Forti G, et al. Cytotoxic activity and transformation of BALB/c 3T3 cells in vitro by the insecticide acephate. Cancer Lett. 1996;106:147–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
