HCV proteins and immunoglobulin variable gene (IgV) subfamilies in HCV-induced type II mixed cryoglobulinemia: a concurrent pathogenetic role
- PMID: 22690241
- PMCID: PMC3368339
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/705013
HCV proteins and immunoglobulin variable gene (IgV) subfamilies in HCV-induced type II mixed cryoglobulinemia: a concurrent pathogenetic role
Abstract
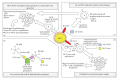
The association between hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and type II mixed cryoglobulinemia (MCII) is well established, but the role played by distinct HCV proteins and by specific components of the anti-HCV humoral immune response remains to be clearly defined. It is widely accepted that HCV drives the expansion of few B-cell clones expressing a restricted pool of selected immunoglobulin variable (IgV) gene subfamilies frequently endowed with rheumatoid factor (RF) activity. Moreover, the same IgV subfamilies are frequently observed in HCV-transformed malignant B-cell clones occasionally complicating MCII. In this paper, we analyze both the humoral and viral counterparts at the basis of cryoglobulins production in HCV-induced MCII, with particular attention reserved to the single IgV subfamilies most frequently involved.
Figures
References
-
- Trejo O, Ramos-Casals M, Garcia-Carrasco M, et al. Cryoglobulinemia: study of etiologic factors and clinical and immunologic features in 443 patients from a single center. Medicine. 2001;80(4):252–262. - PubMed
-
- Ferri C, Sebastiani M, Giuggioli D, et al. Mixed cryoglobulinemia: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 231 patients. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2004;33(6):355–374. - PubMed
-
- Authier FJ, Pawlotsky JM, Viard JP, Guillevin L, Degos JD, Gherardi RK. High incidence of hepatitis C virus infection in patients with cryoglobulinemic neuropathy. Annals of Neurology. 1993;34(5):749–750. - PubMed
-
- Daghestani L, Pomeroy C. Renal manifestations of hepatitis C infection. American Journal of Medicine. 1999;106(3):347–354. - PubMed
-
- Dammacco F, Sansonno D. Mixed cryoglobulinemia as a model of systemic vasculitis. Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology. 1997;15(1):97–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

