A Randomized Multicenter Study Comparing a Tacrolimus-Based Protocol with and without Steroids in HCV-Positive Liver Allograft Recipients
- PMID: 22690326
- PMCID: PMC3368368
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/894215
A Randomized Multicenter Study Comparing a Tacrolimus-Based Protocol with and without Steroids in HCV-Positive Liver Allograft Recipients
Abstract
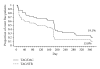
Allograft reinfection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) occurs universally in liver transplant recipients. Corticosteroids can contribute to HCV recurrence. This randomized study evaluated HCV recurrence in HCV-positive liver allograft recipients using steroid-free immunosuppression. All patients received tacrolimus (TAC) at an initial dose of 0.10-0.15 mg/kg. The steroid-free arm (TAC/daclizumab (TAC/DAC, n = 67)) received daclizumab induction, and the steroid arm (TAC/steroid (TAC/STR, n = 68)) received a steroid bolus (≤ 500mg) followed by 15-20 mg/day with discontinuation after month 3. Median HCV viral load at month 12, the primary endpoint, was similar at 5.46 (0.95-6.54) IU/mL with TAC/DAC and 5.91 (0.95-6.89) IU/mL with TAC/STR. Small numerical differences in the estimated rate of freedom from HCV recurrence (19.1 versus 13.8%) and freedom from biopsy proven rejection (78.4 versus 66.1%) were observed between TAC/DAC and TAC/STR. Patient survival estimates were significantly lower with TAC/DAC than with TAC/STR (83.1 versus 95.5%; 95% CI, -0.227 to -0.019%), and graft survival was numerically lower (80.1 versus 91.1%, P = NS). Completion rates (45 versus 82%) indicated poorer tolerability with TAC/DAC than with TAC/STR. Steroid-free immunosuppression had no real impact on HCV viral load. HCV recurrence was higher with TAC/STR. Results are inconclusive due to the unexpected lower completion rates in the TAC/DAC arm.
Figures
References
-
- Wiesner RH, Sorrell M, Villamil F, et al. Report of the first international liver transplantation society expert panel consensus conference on liver transplantation and hepatitis C. Liver Transplantation. 2003;9(11):S1–S9. - PubMed
-
- Brown RS. Hepatitis C and liver transplantation. Nature. 2005;436(7053):973–978. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer M, Crippin J, Gish R, et al. A model to predict severe HCV-related disease following liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2003;38(1):34–41. - PubMed
-
- Feray C, Gigou M, Samuel D, et al. The course of hepatitis C virus infection after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1994;20(5):1137–1143. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer M, Prieto M, Sanjuan F, Rayon JM, Benlloch S, Berenguer J. Effect of calcineurin inhibitors on survival and histologic disease severity in HCV-infected liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplantation. 2006;12, article 762 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

