Investigation of the role of endosomal Toll-like receptors in murine collagen-induced arthritis reveals a potential role for TLR7 in disease maintenance
- PMID: 22691272
- PMCID: PMC3446525
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3875
Investigation of the role of endosomal Toll-like receptors in murine collagen-induced arthritis reveals a potential role for TLR7 in disease maintenance
Abstract
Introduction: Endosomal toll-like receptors (TLRs) have recently emerged as potential contributors to the inflammation observed in human and rodent models of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aims to evaluate the role of endosomal TLRs and in particular TLR7 in the murine collagen induced arthritis (CIA) model.
Methods: CIA was induced by injection of collagen in complete Freund's adjuvant. To investigate the effect of endosomal TLRs in the CIA model, mianserin was administered daily from the day of disease onset. The specific role of TLR7 was examined by inducing CIA in TLR7-deficient mice. Disease progression was assessed by measuring clinical score, paw swelling, serum anti-collagen antibodies histological parameters, cytokine production and the percentage of T regulatory (Treg) cells.
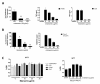
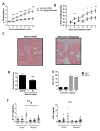
Results: Therapeutic administration of mianserin to arthritic animals demonstrated a highly protective effect on paw swelling and joint destruction. TLR7-/- mice developed a mild arthritis, where the clinical score and paw swelling were significantly compromised in comparison to the control group. The amelioration of arthritis by mianserin and TLR7 deficiency both corresponded with a reduction in IL-17 responses, histological and clinical scores, and paw swelling.
Conclusions: These data highlight the potential role for endosomal TLRs in the maintenance of inflammation in RA and support the concept of a role for TLR7 in experimental arthritis models. This study also illustrates the potential benefit that may be afforded by therapeutically inhibiting the endosomal TLRs in RA.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

