Revised mechanism of complement lectin-pathway activation revealing the role of serine protease MASP-1 as the exclusive activator of MASP-2
- PMID: 22691502
- PMCID: PMC3387078
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202588109
Revised mechanism of complement lectin-pathway activation revealing the role of serine protease MASP-1 as the exclusive activator of MASP-2
Abstract
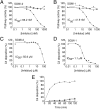
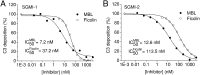
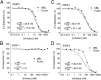
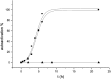
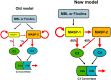
The lectin pathway of complement activation is an important component of the innate immune defense. The initiation complexes of the lectin pathway consist of a recognition molecule and associated serine proteases. Until now the autoactivating mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease (MASP)-2 has been considered the autonomous initiator of the proteolytic cascade. The role of the much more abundant MASP-1 protease was controversial. Using unique, monospecific inhibitors against MASP-1 and MASP-2, we corrected the mechanism of lectin-pathway activation. In normal human serum, MASP-2 activation strictly depends on MASP-1. MASP-1 activates MASP-2 and, moreover, inhibition of MASP-1 prevents autoactivation of MASP-2. Furthermore we demonstrated that MASP-1 produces 60% of C2a responsible for C3 convertase formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: D.H., P.G., G.P., and P.Z. filed patent application for the SGMI inhibitors.
Figures

References
-
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820. - PubMed
-
- Thiel S. Complement activating soluble pattern recognition molecules with collagen-like regions, mannan-binding lectin, ficolins and associated proteins. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:3875–3888. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Matsushita M, Fujita T. The role of ficolins in the lectin pathway of innate immunity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:705–712. - PubMed
-
- Hansen S, et al. Collectin 11 (CL-11, CL-K1) is a MASP-1/3-associated plasma collectin with microbial-binding activity. J Immunol. 2010;185:6096–6104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

