The critically-ill pediatric hemato-oncology patient: epidemiology, management, and strategy of transfer to the pediatric intensive care unit
- PMID: 22691690
- PMCID: PMC3423066
- DOI: 10.1186/2110-5820-2-14
The critically-ill pediatric hemato-oncology patient: epidemiology, management, and strategy of transfer to the pediatric intensive care unit
Abstract
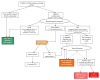
Cancer is a leading cause of death in children. In the past decades, there has been a marked increase in overall survival of children with cancer. However, children whose treatment includes hematopoietic stem cell transplantation still represent a subpopulation with a higher risk of mortality. These improvements in mortality are accompanied by an increase in complications, such as respiratory and cardiovascular insufficiencies as well as neurological problems that may require an admission to the pediatric intensive care unit where most supportive therapies can be provided. It has been shown that ventilatory and cardiovascular support along with renal replacement therapy can benefit pediatric hemato-oncology patients if promptly established. Even if admissions of these patients are not considered futile anymore, they still raise sensitive questions, including ethical issues. To support the discussion and potentially facilitate the decision-making process, we propose an algorithm that takes into account the reason for admission (surgical versus medical) and the hemato-oncological prognosis. The algorithm then leads to different types of admission: full-support admission, "pediatric intensive care unit trial" admission, intensive care with adapted level of support, and palliative intensive care. Throughout the process, maintaining a dialogue between the treating physicians, the paramedical staff, the child, and his parents is of paramount importance to optimize the care of these children with complex disease and evolving medical status.
Figures
References
-
- Steliarova-Foucher E, Stiller C, Kaatsch P, Berrino F, Coebergh JW, Lacour B, Parkin M. Geographical patterns and time trends of cancer incidence and survival among children and adolescents in Europe since the 1970s (the ACCIS project): an epidemiological study. Lancet. 2004;364:2097–2105. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17550-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

