Increased dopamine receptor activity in the nucleus accumbens shell ameliorates anxiety during drug withdrawal
- PMID: 22692565
- PMCID: PMC3442355
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.97
Increased dopamine receptor activity in the nucleus accumbens shell ameliorates anxiety during drug withdrawal
Abstract
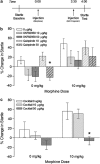
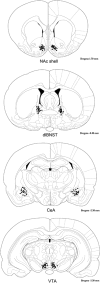
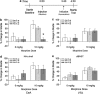
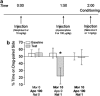
A number of lines of evidence suggest that negative emotional symptoms of withdrawal involve reduced activity in the mesolimbic dopamine system. This study examined the contribution of dopaminergic signaling in structures downstream of the ventral tegmental area to withdrawal from acute morphine exposure, measured as potentiation of the acoustic startle reflex. Systemic administration of the general dopamine receptor agonist apomorphine or a cocktail of the D1-like receptor agonist SKF82958 and the D2-like receptor agonist quinpirole attenuated potentiated startle during morphine withdrawal. This effect was replicated by apomorphine infusion into the nucleus accumbens shell. Finally, apomorphine injection was shown to relieve startle potentiation during nicotine withdrawal and conditioned place aversion to morphine withdrawal. These results suggest that transient activation of the ventral tegmental area mesolimbic dopamine system triggers the expression of anxiety and aversion during withdrawal from multiple classes of abused drugs.
Figures
References
-
- Acquas E, Carboni E, Di Chiara G. Profound depression of mesolimbic dopamine release after morphine withdrawal in dependent rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991;193:133–134. - PubMed
-
- Acquas E, Carboni E, Leone P, Di Chiara G. SCH 23390 blocks drug-conditioned place-preference and place-aversion: anhedonia (lack of reward) or apathy (lack of motivation) after dopamine-receptor blockade. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1989;99:151–155. - PubMed
-
- Acquas E, Di Chiara G. Depression of mesolimbic dopamine transmission and sensitization to morphine during opiate abstinence. J Neurochem. 1992;58:1620–1625. - PubMed
-
- Baker TB, Piper ME, McCarthy DE, Majeskie MR, Fiore MC. Addiction motivation reformulated: an affective processing model of negative reinforcement. Psychol Rev. 2004;111:33–51. - PubMed

