Transient receptor potential channels mediate the tussive response to prostaglandin E2 and bradykinin
- PMID: 22693178
- PMCID: PMC3446777
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-201443
Transient receptor potential channels mediate the tussive response to prostaglandin E2 and bradykinin
Abstract
Background: Cough is the most frequent reason for consultation with a family doctor, or with a general or respiratory physician. Treatment options are limited and a recent meta-analysis concluded that over-the-counter remedies are ineffective and there is increasing concern about their use in children. Endogenous inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and bradykinin (BK), which are often elevated in respiratory disease states, are also known to cause cough by stimulating airway sensory nerves. However, how this occurs is not understood.
Methods: We hypothesised that the transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, TRPA1 and TRPV1, may have a role as 'common effectors' of tussive responses to these agents. We have employed a range of in vitro imaging and isolated tissue assays in human, murine and guinea pig tissue and an in vivo cough model to support this hypothesis.
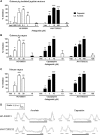
Results: Using calcium imaging we demonstrated that PGE2 and BK activated isolated guinea pig sensory ganglia and evoked depolarisation (activation) of vagal sensory nerves, which was inhibited by TRPA1 and TRPV1 blockers (JNJ17203212 and HC-030031). These data were confirmed in vagal sensory nerves from TRPA1 and TRPV1 gene deleted mice. TRPV1 and TRPA1 blockers partially inhibited the tussive response to PGE2 and BK with a complete inhibition obtained in the presence of both antagonists together in a guinea pig conscious cough model.
Conclusion: This study identifies TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels as key regulators of tussive responses elicited by endogenous and exogenous agents, making them the most promising targets currently identified in the development of anti-tussive drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- McCormick A, Fleming DM, Charlton J; Office of Population Censuses and Surveys Morbidity Statistics from General Practice, Fourth National Study 1991–1992 (Series MB5 No 3). London: HMSO, 1995
-
- Irwin RS, Corrao WM, Pratter MR. Chronic persistent cough in the adult: the spectrum and frequency of causes and successful outcome of specific therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis 1981;123:413–17 - PubMed
-
- Canning BJ, Chou Y-L. Cough sensors. I. Physiological and pharmacological properties of the afferent nerves regulating cough. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2009;187:23–47 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
