Diagnosis of fanconi anemia: chromosomal breakage analysis
- PMID: 22693659
- PMCID: PMC3368163
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/238731
Diagnosis of fanconi anemia: chromosomal breakage analysis
Abstract
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare inherited syndrome with diverse clinical symptoms including developmental defects, short stature, bone marrow failure, and a high risk of malignancies. Fifteen genetic subtypes have been distinguished so far. The mode of inheritance for all subtypes is autosomal recessive, except for FA-B, which is X-linked. Cells derived from FA patients are-by definition-hypersensitive to DNA cross-linking agents, such as mitomycin C, diepoxybutane, or cisplatinum, which becomes manifest as excessive growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest, and chromosomal breakage upon cellular exposure to these drugs. Here we provide a detailed laboratory protocol for the accurate assessment of the FA diagnosis as based on mitomycin C-induced chromosomal breakage analysis in whole-blood cultures. The method also enables a quantitative estimate of the degree of mosaicism in the lymphocyte compartment of the patient.
Figures
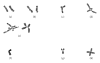
References
-
- Giampietro PF, Adler-Brecher B, Verlander PC, Pavlakis SG, Davis JG, Auerbach AD. The need for more accurate and timely diagnosis in Fanconi anemia: a report from the International Fanconi Anemia Registry. Pediatrics. 1993;91(6):1116–1120. - PubMed
-
- Giampietro PF, Verlander PC, Davis JG, Auerbach AD. Diagnosis of Fanconi anemia in patients without congenital malformations: an International Fanconi Anemia Registry Study. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1997;68(1):58–61. - PubMed
-
- Alter BP. Cancer in Fanconi anemia, 1927–2001. Cancer. 2003;97(2):425–440. - PubMed
-
- Alter BP. Bone marrow failure: a child is not just a small adult (but an adult can have a childhood disease) Hematology. 2005:96–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

