A medley of midbrain maladies: a brief review of midbrain anatomy and syndromology for radiologists
- PMID: 22693668
- PMCID: PMC3366251
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/258524
A medley of midbrain maladies: a brief review of midbrain anatomy and syndromology for radiologists
Abstract
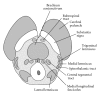
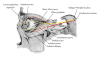
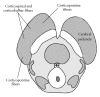
The midbrain represents the uppermost portion of the brainstem, containing numerous important nuclei and white matter tracts, most of which are involved in motor control, as well as the auditory and visual pathways. Notable midbrain nuclei include the superior and inferior colliculus nuclei, red nucleus, substantia nigra, oculomotor nuclear complex, and trochlear nucleus. In addition, white matter tracts include the brachium conjunctivum, medial and lateral lemniscus, spinothalamic tracts, and the fiber tracts within the cerebral peduncles. Although neurologically vital, many of these small midbrain nuclei and white matter tracts are not easily individually identified on neuroimaging. However, given their diverse functions, midbrain pathology often leads to distinct clinical syndromes. A review and understanding of the location and relationships between the different midbrain nuclei and fiber tracts will allow more precise correlation of radiologic findings with patient pathology and symptomatology. Particular syndromes associated with midbrain pathology include the Weber, Claude, Benedikt, Nothnagel, and Parinaud syndromes. The oculomotor and trochlear cranial nerves also reside at this level. An understanding of their functions as well as their projected courses from the midbrain towards the eye allows identification of distinct locations which are particularly vulnerable to pathology.
Figures






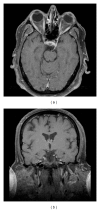



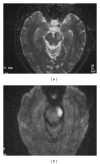
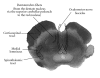

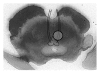


References
-
- Hathout G. Clinical Neuroradiology: A Case-Based Approach. Cambridge University Press; 2009.
-
- Afifi AK, Bergman RA. Functional Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas. McGraw-Hill Companies; 1998.
-
- Campbell WW, DeJong RN, Haerer AF. DeJong’s the Neurologic Examination. 6th edition. Lippincott Williayms & Wilkins; 2005.
-
- Kim JS, Kim J. Pure midbrain infarction: clinical, radiologic, and pathophysiologic findings. Neurology. 2005;64(7):1227–1232. - PubMed
-
- Cho BK, Wang KC, Nam DH, et al. Pineal tumors: experience with 48 cases over 10 years. Child’s Nervous System. 1998;14(1-2):53–58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

