Cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes in Bangladesh: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies between 1995 and 2010
- PMID: 22694854
- PMCID: PMC3487781
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-434
Cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes in Bangladesh: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies between 1995 and 2010
Abstract
Background: Belief is that chronic disease prevalence is rising in Bangladesh since death from them has increased. We reviewed published cardiovascular (CVD) and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) studies between 1995 and 2010 and conducted a meta-analysis of disease prevalence.
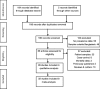
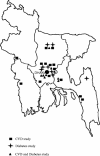
Methods: A systematic search of CVD and T2DM studies yielded 29 eligible studies (outcome: CVD only = 12, T2DM only = 9, both = 8). Hypertension (HTN) was the primary outcome of CVD studies. HTN and T2DM were defined with objective measures and standard cut-off values. We assessed the study quality based on sampling frame, sample size, and disease evaluation. Random effects models calculated pooled disease prevalence (95% confidence interval) in studies with general population samples (n = 22).
Results: The pooled HTN and T2DM prevalence were 13.7% (12.1%-15.3%) and 6.7% (4.9%-8.6%), respectively. Both diseases exhibited a secular trend by 5-year intervals between 1995 and 2010 (HTN = 11.0%, 12.8%, 15.3%, T2DM = 3.8%, 5.3%, 9.0%). HTN was higher in females (M vs. F: 12.8% vs.16.1%) but T2DM was higher in males (M vs. F: 7.0% vs. 6.2%) (non-significant). Both HTN and T2DM were higher in urban areas (urban vs. rural: 22.2% vs. 14.3% and 10.2% vs. 5.1% respectively) (non-significant). HTN was higher among elderly and among working professionals. Both HTN and T2DM were higher in 'high- quality' studies.
Conclusions: There is evidence of a rising secular trend of HTN and T2DM prevalence in Bangladesh. Future research should focus on the evolving root causes, incidence, and prognosis of HTN and T2DM.
Figures

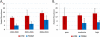
References
-
- Laskar SI. Urbanization in Bangladesh: some contemporary observations. Bangladesh Dev Stud. 1996;24:207–216. - PubMed
-
- Dewan AM, Yamaguchi Y. Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Applied Geography. 2009;29:390–401. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2008.12.005. - DOI
-
- Alam JBM, Alam MJB, Rahman MH, Khan SK, Munna GM. Unplanned urbanization: Assessment through calculation of environmental degradation index. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. 2006;3:119–130.
-
- Islam N, Ullah GMS. Factors affecting consumers’ preferences on fast food items in Bangladesh. Journal of Applied Business Research. 2010;26:131–147.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

