A patient with primary Burkitt's lymphoma of the postnasal space: case report
- PMID: 22695293
- PMCID: PMC3414781
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-3284-4-33
A patient with primary Burkitt's lymphoma of the postnasal space: case report
Expression of concern in
-
Comment: Head and Neck Oncology.BMC Med. 2014 Feb 5;12:24. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-12-24. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 24499430 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Introduction: Burkitt's lymphoma is a highly aggressive lymphoma. The endemic form is present with Epstein - Barr virus. The most common sites are the mandible, facial bones, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, ovaries, breast and extra-nodal sites. We present the first reported case of a primary Burkitt's lymphoma of the postnasal space occurring in an elderly Caucasian male.
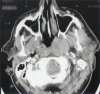
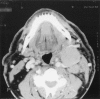
Case presentation: A 72-year-old Caucasian male farmer presented with a 6-week history of a productive cough and a painless left sided cervical swelling. Examination of the neck revealed a 5 cm by 5 cm hard mass in the left anterior triangle. A CT scan of the head and neck showed a soft tissue swelling in the postnasal space. Histology of the postnasal space mass showed squamous mucosa infiltrated by a high grade lymphoma. Immunohistochemical staining and in situ hybridisation confirmed the tumour to be Epstein - Barr virus Ribonucleic acid negative suggesting this was a rare sporadic form of the tumour presenting in a location that is atypical for the clinical subtype and age of the patient.
Conclusion: This is the first reported case of sporadic Burkitt's lymphoma of the postnasal space of an elderly Caucasian male in the absence of Epstein - Barr virus or human immunodeficiency virus infection and further serves to illustrate the diversity of histological subtypes of malignancies that may develop at this concealed site.
Figures

References
-
- Diebold J, In: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Jaffe E, Harris N, Stein H, editor. IARC Press, Washington, DC; 2001. Burkitt’s lymphoma; pp. 181–184.
-
- Kasamon YL, Swinnen LJ. Treatment advance in adult Burkitt’s lymphoma and Leukaemia. Curr Opin Oncol. 2004;16:426–435. - PubMed
-
- Isaacson P, Norton A. Extra nodal Lymphomas. Churchill Livingstone, London; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

