Interventional radiology at the meetings of the German Radiological Society from 1998 to 2008: evaluation of structural changes and radiation issues
- PMID: 22696003
- PMCID: PMC3292639
- DOI: 10.1007/s13244-011-0138-8
Interventional radiology at the meetings of the German Radiological Society from 1998 to 2008: evaluation of structural changes and radiation issues
Abstract
Objectives: Evaluation of structural changes and the weight given to radiation exposure of interventional radiology (IR) contributions at the Congress of the German Radiological Association from 1998 to 2008.
Methods: All IR abstracts were evaluated for type of contribution, design, imaging modality, and anatomic region. Weight given to radiation exposure was recorded as general statement, main topic and/or dose reduction. Statistical analysis included calculation of absolute/relative proportions of subgroups and ANOVA regression analyses.
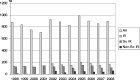
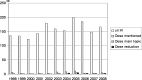
Results: Out of 9,436 abstracts, 1,728 (18%) were IR-related. IR abstracts significantly rose to a maximum of 200 (20%) in 2005 (P = 0.048). While absolute numbers of scientific contributions declined, educational contributions significantly increased (P = 0.003). Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were the main IR imaging modalities, with growing use of CT (P = 0.021). The main body regions were vessels (45%) and abdomen (31%). Radiation exposure was addressed as a general statement in 3% of abstracts, as a main topic in 2%, and for dose reduction in 1%, respectively. During the study interval a significant growth of dose reduction abstracts was observed (P = 0.016).
Conclusions: IR emerged as a growing specialty of radiology, with a significant increase in educational contributions. Radiation exposure was rarely in the focus of interest but contributions relating to dose reduction demonstrated a significant growth during the study period. Main Messages • Interventional radiology emerged as a growing specialty at the German radiological congress. • Significant increments of educational and prospective research contributions could be observed. • Despite a significant trend towards computed tomography, radiation exposure of IR was rarely in the focus of interest. • Contributions related to dose reduction demonstrated a significant growth during the study period.
Figures




References
-
- Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Smith HS, Hirsch JA. Analysis of growth of interventional techniques in managing chronic pain in the medicare population: a 10-year evaluation from 1997 to 2006. Pain Physician. 2009;12:9–34. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien J, Baerlocher MO, Asch MR, Hayeems E, Kachura JR, Collingwood P. Limitations influencing interventional radiology in Canada: results of a national survey by the Canadian Interventional Radiology Association (Cira) Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007;30:847–853. doi: 10.1007/s00270-007-9084-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

