Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver metastases from colorectal cancer
- PMID: 22696357
- PMCID: PMC11931680
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006317.pub3
Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver metastases from colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most common malignant tumour and the third leading cause of cancer deaths in USA. For advanced CRC, the liver is the first site of metastatic disease; approximately 50 % of patients with CRC will develop liver metastases either synchronously or metachronously within 2 years after primary diagnosis. Hepatic resection (HR) is the only curative option, but only 15-20% of patients with liver metastases from CRC (CRLMs) are suitable for surgical standard treatment. In patients with unresectable CRLMs downsizing chemotherapy can improve resectability (16%). Modern systemic chemotherapy represents the only significant treatment for unresectable CRLMs. However several loco-regional treatments have been developed: hepatic arterial infusion (HAI), cryosurgical ablation (CSA), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation and selective internal radion treatment (SIRT). During the past decade RFA has superseded other ablative therapies, due to its low morbidity, mortality, safety and patient acceptability.
Objectives: The objective of this study was to systematically review the role of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in the treatment of CRLMs.
Search methods: We performed electronic searches in the following databases:CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE. Current trials were identified through the Internet using the Clinical-Trials.gov site (to January 2, 2012) and ASCO Proceedings. The reference lists of identified trials were reviewed for additional studies.
Selection criteria: Randomized clinical trials (RCTs), quasi-randomised or controlled clinical trials (CCTs) comparing RFA to any other therapy for CRLMs were included. Observational study designs including comparative cohort studies comparing RFA to another intervention, single arm cohort studies or case control studies have been included if they have: prospectively collected data, ten or more patients; and have a mean or median follow-up time of 24 months. Patients with CRLMs who have no contraindications for RFA. Patients with unresectable extra-hepatic disease were also included.Trials have been considered regardless of language of origin.
Data collection and analysis: A total of 1144 records were identified through the above electronic searching. We included 18 studies: 10 observational studies, 7 Clinical Controlled Trials (CCTs) and an additional 1 Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT) (abstract) identified by hand searching in the 2010 ASCO Annual Meeting. The most appropriate way of summarizing time-to-event data is to use methods of survival analysis and express the intervention effect as a hazard ratio. In the included studies these outcome are mostly reported as dichotomous data so we should have asked authors research data for each participant and perform Individual Patient Data (IPD) meta-analysis. Given the study design and low quality of included studies we decided to give up and not to summarize these data.
Main results: Seventeen studies were not randomised and this increases the potential for selection bias. In addition, there was imbalance in the baseline characteristics of the participants included in all studies. All studies were classified as having a elevate risk of bias. The assessment of methodological quality of all non-randomized studies included in meta-analysis performed by the STROBE checklist has allowed us to identify several methodological limits in most of the analysed studies. At present, the information from the single RCT included (Ruers 2010) comes from an abstract of 2010 ASCO Annual Meeting where the allocation concealment was not reported; however in original protocol allocation concealment was adequately reported (EORTC 40004 protocol). The heterogeneity regarding interventions, comparisons and outcomes rendered the data not suitable.
Authors' conclusions: This systematic review gathers information from several controlled clinical trials and observational studies which are vulnerable to different types of bias. The imbalance between characteristics of patients in the allocated groups appears to be the main concern. Only one randomised clinical trial (published as an abstract), comparing 60 patients receiving RFA plus CT versus 59 patients receiving CT alone, was identified. This study showed that PFS was significantly higher in the group that received RFA. However, it was not able to provide information on overall survival. In conclusion, evidence from the included studies are insufficient to recommend RFA for a radical oncological treatment of CRLMs.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures

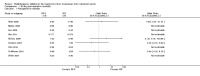



Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006317.pub2
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdalla 2004 {published data only}
Aloia 2006 {published data only}
-
- Aloia TA, Vauthey JN, Loyer EM, Ribero D, Pawlik TM, Wei SH, et al. Solitary colorectal liver metastasis. Resection determines outcome. Archives of Surgery 2006;141:460‐7. - PubMed
Berber 2008 {published data only}
-
- Berber E, Tsinberg M, Tellioglu G, Simpfendorfer CH, Siperstein AE. Resection versus laparoscopic radiofrequency thermal ablation of solitary colorectal liver metastasis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2008;12:1976‐82. - PubMed
Gleisner 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gleisner AL, Choti MA, Assumpcao L, Nathan H, Schulick RD, Pawlik TM. Colorectal liver metastases: recurrence and survival following hepatic resection, radiofrequency ablation, and combined resection‐radiofrequency ablation.. Archives of Surgery 2008;143:1204‐12. - PubMed
Hur 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hur H, Ko YT, Min BS, Kim KS, Choi JS, Sohn SK, et al. Comparative study of resection and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of solitary colorectal liver metastases. America Journal of Surgery 2009;197:728‐36. - PubMed
Kim 2011 {published data only}
Kornprat 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kornprat P, Jarnagin WR, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Blumgart LH, D'Angelica M. Role of intraoperative thermoablation combined with resection in the treatment of hepatic metastasis from colorectal cancer. Archives of Surgery 2007;142:1087‐92. - PubMed
Lee 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lee WS, Yun SH, Chun HK, Lee WY, Kim SJ, Choi SH, et al. Clinical outcomes of hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation in patients with solitary colorectal liver metastasis. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2008;42:945‐9. - PubMed
McKay 2009 {published data only}
Oshowo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Oshowo A, Gillams A, Harrison E, Lees WR, Taylor I. Comparison of resection and radiofrequency ablation for treatment of solitary colorectal liver metastases. British Journal of Surgery 2003;90:1240‐3. - PubMed
Otto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Otto G, Duber C, Hoppe‐Lotichius M, Konig J, Heise M, Pitton MB. Radiofrequency ablation as first‐line treatment in patients with early colorectal liver metastases amenable to surgery. Annals of Surgery 2010;251:796‐803. - PubMed
Park 2008 {published data only}
-
- Park IJ, Kim HC, Yu CS, Kim PN, Won HJ, Kim JC. Radiofrequency ablation for metachronous liver metastasis from colorectal cancer after curative surgery. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2008;15:227‐32. - PubMed
Reuter 2009 {published data only}
-
- Reuter NP, Woodall CE, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM, Martin RCG. Radiofrequency ablation vs. resection for hepatic colorectal metastasis: therapeutically equivalent?. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2009;13:486‐91. - PubMed
Ruers 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ruers T, Punt CJ, Coevorden F, Borel Rinkes I, Ledermann JA, Poston GJ, et al. Final results of the EORTC intergroup randomized study 40004 (CLOCC) evaluating the benefit of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) combined with chemotherapy for unresectable colorectal liver metastases (CRC LM). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(15s:suppl):abstr 3526.
Scaife 2003 {published data only}
-
- Scaife CL, Curley SA, Izzo F, Marra P, Delrio P, Daniele B, et al. Feasibility of adjuvant hepatic arterial infusion of chemotherapy after radiofrequency ablation with or without resection in patients with hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2003;10:348‐54. - PubMed
Schiffman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schiffman SC, Bower M, Brown RE, Martin RC, McMasters KM, Scoggins CR. Hepatectomy is superior to thermal ablation for patients with a solitary colorectal liver metastasis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2010;14:1881‐6. - PubMed
Vyslouzil 2009 {published data only}
-
- Vyslouzil K, Klementa I, Starý L, Zboril P, Skalický P, Dlouhý M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Zentralbl Chir 2009;134:145‐8. - PubMed
White 2007 {published data only}
-
- White RR, Avital I, Sofocleous CT, Brown KT, Brody LA, Covey A, et al. Rates and patterns of recurrence for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and open wedge resection for solitary colorectal liver metastasis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2007;11:256‐63. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Al‐Asfoor 2008 {published data only}
Curley 2008 {published data only}
de Jong 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jong MC, Pulitano C, Ribero D, Strub J, Mentha G, Schulick RD, et al. Rates and patterns of recurrence following curative intent surgery for colorectal liver metastasis: an international multi‐institutional analysis of 1669 patients. Annals of Surgery 2009;250:440‐8. - PubMed
Doyle 2010 {published data only}
-
- Doyle MB, Chapman WC. Radiofrequency ablation for resectable colorectal hepatic metastases: is it time for a randomized controlled trial?. Annals of Surgery 2010;251:803‐6. - PubMed
Elias 2004 {published data only}
-
- Elias D, Baton O, Sideris L, Matsuhisa T, Pocard M, Lasser P. Local recurrences after intraoperative radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases: a comparative study with anatomic and wedge resections. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2004;11:500‐5. - PubMed
Frich 2008a {published data only}
-
- Frich L. Local ablation of colorectal liver metastases ‐ a systematic review. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 2008;128:54‐6. - PubMed
Frich 2008b {published data only}
-
- Frich L, Brabrand K, Aalokken TM, Edwin B, Gladhaug IP. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 2008;128:57‐60. - PubMed
Grundmann 2007 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann RT. Liver metastases of colorectal carcinoma‐‐may the DRG‐system influence the operative procedure?. Zentralblatt fur Chirurgie 2007;132:287‐92. - PubMed
Jansen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jansen MC, Wanrooy S, Hillegersberg R, Rijken AM, Coevorden F, Prevoo W, et al. Assessment of systemic inflammatory response (SIR) in patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation or partial liver resection for liver tumors. European Journal of Surgical Oncology 2008;34:662‐7. - PubMed
Joosten 2005 {published data only}
-
- Joosten J, Jager G, Oyen W, Wobbes T, Ruers T. Cryosurgery and radiofrequency ablation for unresectable colorectal liver metastases. European Journal of Surgical Oncology 2005;31:1152‐9. - PubMed
Leblanc 2008 {published data only}
-
- Leblanc F, Fonck M, Brunet R, Becouarn Y, Mathoulin‐Pelissier S, Evrard S. Comparison of hepatic recurrences after resection or intraoperative radiofrequency ablation indicated by size and topographical characteristics of the metastases. European Journal of Surgical Oncology 2008;34:185‐90. - PubMed
Leen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Leen E, Horgan PG. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Surgical Oncology 2007;16:47‐51. - PubMed
Lupo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lupo L, Gallerani A, Panzera P, Tandoi F, Palma G, Memeo V. Randomized clinical trial of radiofrequency‐assisted versus clamp‐crushing liver resection. British Journal of Surgery 2007;94:287‐91. - PubMed
Martin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Martin RC, Scoggins CR, McMasters KM. A phase II study of radiofrequency ablation of unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer with hepatic arterial infusion pump chemotherapy. Journal of Surgical Oncology 2006;93:387‐93. - PubMed
Mulier 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J, Michel L, Marchal G, Ruers T. Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for resectable colorectal liver metastases: time for a randomized trial?. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2008;15:144‐57. - PubMed
Pawlik 2003 {published data only}
Reurs 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ruers TJ, Joosten JJ, Wiering B, Langenhoff BS, Dekker HM, Wobbes T, Oyen WJ, et al. Comparison between local ablative therapy and chemotherapy for non‐resectable colorectal liver metastases: a prospective study. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2007;14:1161‐9. - PubMed
Scott 2001 {published data only}
-
- Scott DJ, Young WN, Watumull LM, Lindberg G, Fleming JB, Huth JF, et al. Accuracy and effectiveness of laparoscopic vs open hepatic radiofrequency ablation. Surgical Endoscopy 2001;15:135‐40. - PubMed
Stang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Stang A, Fischbach R, Teichmann W, Bokemeyer C, Braumann D. A systematic review on the clinical benefit and role of radiofrequency ablation as treatment of colorectal liver metastases. European Journal of Cancer 2009;45:1748‐56. - PubMed
Sutherland 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sutherland LM, Williams JA, Padbury RT, Gotley DC, Stokes B, Maddern GJ. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: a systematic review. Archives of Surgery 2006;141:181‐90. - PubMed
Tez 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tez M, Tez S. Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for resectable colorectal liver metastases: time for a randomized trial?. Annals of Surgical Oncolology 2008;15:1804. - PubMed
Wong 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wong SL, Mangu PB, Choti MA, Crocenzi TS, Dodd GD 3rd, Dorfman GS, et al. 2009 clinical evidence review on radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28:493‐508. - PubMed
Additional references
Adam 2004
Adam 2009
-
- Adam R, Wicherts DA, Haas RJ, Ciacio O, Lévi F, Paule B, et al. Patients with initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases: is there a possibility of cure?. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009;27:1829‐35. - PubMed
American Cancer Society 2010
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2010. http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@nho/documents/document/acspc‐0....
Bauditz 2011
-
- Bauditz J. Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of metastatic colorectal carcinoma: state of the art despite of missing randomized trials?. Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie 2011;11:624‐6. - PubMed
Benoist 2004
-
- Benoist S, Nordlinger B. Radiofrequency ablation in liver tumours. Annals of Oncology 2004;15(Suppl 4):313–7. - PubMed
Boutros 2010
-
- Boutros C, Somasundar P, Garrean S, Saied A, Espat NJ. Microwave coagulation therapy for hepatic tumors: review of the literature and critical analysis. Surgical Oncolology 2010;19:e22‐32. - PubMed
de Jong 2011
-
- Jong MC, Mayo SC, Pawlik TM. Outcomes of ablation versus resection for colorectal liver metastases. Annals of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2010;252:142‐8..
Decadt 2004
-
- Decadt B, Siriwardena AK. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours: systematic review. Lancet Oncology 2004;5(9):550‐60. - PubMed
Egger 2001
-
- Egger M, Smith GD, Altman DG. Systematic reviews in health care: meta‐analysis in context. Cornwall, England: BMJ Publishing, 2001.
EORTC 40004 protocol
-
- Ruers T, Mauer M, Lentz MA. CLOCC trial (Chemotherapy + Local ablation versus Chemotherapy). Randomized phase II study investigating the role of local treatment of liver metastases by radiofrequency combined with chemotherapy and of chemotherapy alone in patients with unresectable colorectal liver metastases. http://www.eortc.be/protoc/details.asp?protocol=40004 (accessed 1 September 2011).
Erce 2003
-
- Erce C, Parks RW. Interstitial ablative techniques for hepatic tumours. British Journal of Surgery 2003;90:272‐89. - PubMed
Feliberti 2006
-
- Feliberti EC, Wagman LD. Radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Control 2006;13:48‐51. - PubMed
Garcea 2003
-
- Garcea G, Lloyd TD, Aylott C, Maddern G, Berry DP. The emergent role of focal liver ablation techniques in the treatment of primary and secondary liver tumours. European Journal of Cancer 2003;39:2150‐64. - PubMed
Garden 2006
Gillams 2004
-
- Gillams AR, Lees WR. Radio‐frequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases in 167 patients. European Radiolology 2004;14:2261‐7. - PubMed
Gillams 2008
-
- Gillams AR, Lees WR. Five‐year survival following radiofrequency ablation of small, solitary, hepatic colorectal metastases. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 2008;19:712‐7. - PubMed
Goldberg 1998
-
- Goldberg SN, Hahn PF, Tanabe KK, Mueller PR, Schima W, Athanasoulis CA, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency tissue ablation: does perfusion‐mediated tissue cooling limit coagulation necrosis?. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 1998;9:101‐11. - PubMed
Goode 2005
-
- Goode JA, Sabharwal T, Adam A. Percutaneous ablation of hepatic metastases. In: Lencioni R, Cioni D, Bartolozzi C editor(s). Focal liver lesions. Heidelberg: Springer‐Verlag, 2005:337‐48.
Gray 2001
-
- Gray B, Hazel G, Hope M, Burton M, Moroz P, Anderson J, et al. Randomised trial of SIR‐Spheres plus chemotherapy vs. chemotherapy alone for treating patients with liver metastases from primary large bowel cancer. Annals of Oncology 2001;12:1711‐20. - PubMed
Hompes 2011
Idelevich 2009
-
- Idelevich E, Greif F, Mavor E, Miller R, Kashtan H, Susmalian S, Ariche A, Brenner B, Baruch NB, Dinerman M, Shani A. Phase II study of UFT with leucovorin plus hepatic arterial infusion with irinotecan, 5‐fluorouracil and leucovorin for non‐resectable liver metastases of colorectal cancer. Chemotherapy 2009;55:76‐82. - PubMed
Knudsen 2009
-
- Knudsen AR, Kannerup AS, Mortensen FV, Nielsen DT. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases downstaged by chemotherapy. Acta Radiologica 2009;50:716‐21. - PubMed
Lau 2003
-
- Lau TN, Lo RHG, Tan BS. Colorectal hepatic metastases: role of radiofrequency ablation. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore 2003;32:212‐8. - PubMed
Lencioni 2004
-
- Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Cioni D, Della Pina C, Bartolozzi C. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic colorectal metastases: technique, indications, results, and new promises. Investigative Radiology 2004;39:689‐97. - PubMed
Lencioni 2005
-
- Lencioni R, Cioni D, Lera J, Rocchi E, Della Pina C, Crocetti L. Radiofrequency ablation: principles and techniques. In: Lencioni R, Cioni D, Bartolozzi C editor(s). Focal liver lesions. Heidelberg (Germany): Springer‐Verlag, 2005:307‐316.
Lencioni 2009
-
- Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Cioni D. Loco‐regional ablative therapies for colorectal metastases. In: Dionigi R editor(s). Recent advances in liver surgery. Austin (USA): Landes Bioscience, 2009:234‐41.
Machi 2006
-
- Machi J, Oishi AJ, Sumida K, Sakamoto K, Furumoto NL, Oishi RH, et al. Long‐term outcome of radiofrequency ablation for unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer: evaluation of prognostic factors and effectiveness in first‐ and second‐line management. Cancer Journal 2006;12:318–26. - PubMed
McGahan 1996
-
- McGahan JP, Gu WZ, Brock JM, Tesluk H, Jones CD. Hepatic ablation using bipolar radiofrequency electrocautery. Academic Radiolology 1996;3:418‐22. - PubMed
Moher 2009
Mulier 2005
Mulier 2008a
-
- Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J, Michel L, Marchal G, Ruers T. Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for resectable colorectal liver metastases: time for a randomized trial?. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2008;15:144‐57. - PubMed
Mulier 2008b
-
- Mulier S, Ruers T, Jamart J, Michel L, Marchal G, Ni Y. Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for resectable colorectal liver metastases: time for a randomized trial?. Digestive Surgery 2008;25:445‐60. - PubMed
Schindl 2008
-
- Schindl M, Gruenberger Th, Längle F. Current strategies in the treatment of colorectal cancer liver metastases: aspects of surgical treatment. European Surgery 2008;16:332‐6.
Siperstein 2007
-
- Siperstein AE, Berber E, Ballem N, Parikhn RT. Survival after radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: 10‐year experience. Annals of Surgery 2007;246:559‐65. - PubMed
Solbiati 1997
-
- Solbiati L, Ierace T, Goldberg SN, Sironi S, Livraghi T, Fiocca R, et al. Percutaneous US‐guided radio‐frequency tissue ablation of liver metastases: treatment and follow‐up in 16 patients. Radiology 1997;202:195‐203. - PubMed
Stroup 2000
-
- Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta‐analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta‐analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. Journal of American Medical Association 2000;283:2008‐12. - PubMed
Tooth 2005
-
- Tooth L, Ware R, Bain C, Purdie DM, Dobson A. Quality of reporting of observational longitudinal research. American Journal of Epidemiology 2005;161:280‐8. - PubMed
Tsai 2009
-
- Tsai S, Pawlik TM. Outcomes of ablation versus resection for colorectal liver metastases: are we comparing apples with oranges?. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2009;16:2422‐8. - PubMed
Vandenbroucke 2007
Veltri 2008
-
- Veltri A, Sacchetto P, Tosetti I, Pagano E, Fava C, Gandini G. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases:small size favourably predicts technique effectiveness and survival. Cardiovascular Interventional Radiolology 2008;31:948–56. - PubMed
Weiss 1986
-
- Weiss L, Grundmann E, Torhorst J, Hartveit F, Moberg I, Eder M, et al. Haematogenous metastatic patterns in colonic carcinoma: an analysis of 1541 necropsies. Journal of Pathology 1986;150:195‐203. - PubMed
Whitehead 1991
-
- Whitehead A, Whitehead J. A general parametric approach to the meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials.. Statistics in Medicine 1991;10(11):1665‐77. - PubMed
Wood 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

