8-OH-DPAT abolishes the pulmonary C-fiber-mediated apneic response to fentanyl largely via acting on 5HT1A receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius
- PMID: 22696579
- PMCID: PMC3423994
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00016.2012
8-OH-DPAT abolishes the pulmonary C-fiber-mediated apneic response to fentanyl largely via acting on 5HT1A receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius
Abstract
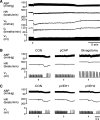
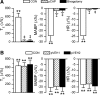
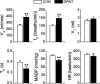
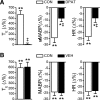
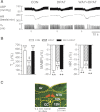
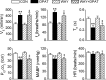
Intravenous bolus injection of morphine causes a vagal-mediated brief apnea (∼3 s), while continuous injection, via action upon central μ-opioid receptor (MOR), arrests ventilation (>20 s) that is eliminated by stimulating central 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors (5HT(1A)Rs). Bronchopulmonary C-fibers (PCFs) are essential for triggering a brief apnea, and their afferents terminate at the caudomedial region of the nucleus tractus solitarius (mNTS) that densely expresses 5HT(1A)Rs. Thus we asked whether the vagal-mediated apneic response to MOR agonists was PCF dependent, and if so, whether this apnea was abolished by systemic administration of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetral (8-OH-DPAT) largely through action upon mNTS 5HT(1A)Rs. Right atrial bolus injection of fentanyl (5.0 μg/kg, a MOR agonist) was performed in the anesthetized and spontaneously breathing rats before and after: 1) selective blockade of PCFs' conduction and subsequent bivagotomy; 2) intravenous administration of 5HT(1A)R agonist 8-OH-DPAT; 3) intra-mNTS injection of 8-OH-DPAT; and 4) intra-mNTS injection of 5HT(1A)R antagonist WAY-100635 followed by 8-OH-DPAT (iv). We found the following: First, fentanyl evoked an immediate apnea (2.5 ± 0.4 s, ∼6-fold longer than the baseline expiratory duration, T(E)), which was abolished by either blocking PCFs' conduction or bivagotomy. Second, this apnea was prevented by systemic 8-OH-DPAT challenge. Third, intra-mNTS injection of 8-OH-DPAT greatly attenuated the apnea by 64%. Finally, intra-mNTS microinjection of WAY-100635 significantly attenuated (58%) the apneic blockade by 8-OH-DPAT (iv). We conclude that the vagal-mediated apneic response to MOR activation depends on PCFs, which is fully antagonized by systemic 8-OH-DPAT challenge largely via acting on mNTS 5HT(1A)Rs.
Figures


References
-
- Aicher SA, Goldberg A, Sharma S, Pickel VM. mu-opioid receptors are present in vagal afferents and their dendritic targets in the medial nucleus tractus solitarius. J Comp Neurol 422: 181– 190, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Belvisi MG, Hele DJ. Cough Sensors. III. Opioid and cannabinoid receptors on vagal sensory nerves. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2009, vol. 187, p. 63– 76 - PubMed
-
- Bianchi AL, Denavit-Saubie M, Champagnat J. Central control of breathing in mammals: neuronal circuitry, membrane properties, and neurotransmitters. Physiol Rev 75: 1– 45, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

