Fission yeast Alp14 is a dose-dependent plus end-tracking microtubule polymerase
- PMID: 22696680
- PMCID: PMC3408415
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0205
Fission yeast Alp14 is a dose-dependent plus end-tracking microtubule polymerase
Abstract
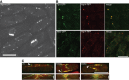
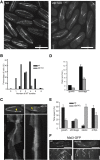
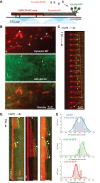
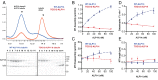
XMAP215/Dis1 proteins are conserved tubulin-binding TOG-domain proteins that regulate microtubule (MT) plus-end dynamics. Here we show that Alp14, a XMAP215 orthologue in fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, has properties of a MT polymerase. In vivo, Alp14 localizes to growing MT plus ends in a manner independent of Mal3 (EB1). alp14-null mutants display short interphase MTs with twofold slower assembly rate and frequent pauses. Alp14 is a homodimer that binds a single tubulin dimer. In vitro, purified Alp14 molecules track growing MT plus ends and accelerate MT assembly threefold. TOG-domain mutants demonstrate that tubulin binding is critical for function and plus end localization. Overexpression of Alp14 or only its TOG domains causes complete MT loss in vivo, and high Alp14 concentration inhibits MT assembly in vitro. These inhibitory effects may arise from Alp14 sequestration of tubulin and effects on the MT. Our studies suggest that Alp14 regulates the polymerization state of tubulin by cycling between a tubulin dimer-bound cytoplasmic state and a MT polymerase state that promotes rapid MT assembly.
Figures


References
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:309–322. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. Microtubule end binding: EBs sense the guanine nucleotide state. Curr Biol. 2011;21:R283–R285. - PubMed
-
- Al-Bassam J, Larsen NA, Hyman AA, Harrison SC. Crystal structure of a TOG domain: conserved features of XMAP215/Dis1-family TOG domains and implications for tubulin binding. Structure. 2007;15:355–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

