Harnessing pain heterogeneity and RNA transcriptome to identify blood-based pain biomarkers: a novel correlational study design and bioinformatics approach in a graded chronic constriction injury model
- PMID: 22697386
- PMCID: PMC5518237
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07833.x
Harnessing pain heterogeneity and RNA transcriptome to identify blood-based pain biomarkers: a novel correlational study design and bioinformatics approach in a graded chronic constriction injury model
Abstract
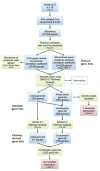
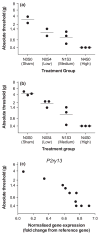
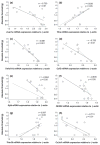
A quantitative, peripherally accessible biomarker for neuropathic pain has great potential to improve clinical outcomes. Based on the premise that peripheral and central immunity contribute to neuropathic pain mechanisms, we hypothesized that biomarkers could be identified from the whole blood of adult male rats, by integrating graded chronic constriction injury (CCI), ipsilateral lumbar dorsal quadrant (iLDQ) and whole blood transcriptomes, and pathway analysis with pain behavior. Correlational bioinformatics identified a range of putative biomarker genes for allodynia intensity, many encoding for proteins with a recognized role in immune/nociceptive mechanisms. A selection of these genes was validated in a separate replication study. Pathway analysis of the iLDQ transcriptome identified Fcγ and Fcε signaling pathways, among others. This study is the first to employ the whole blood transcriptome to identify pain biomarker panels. The novel correlational bioinformatics, developed here, selected such putative biomarkers based on a correlation with pain behavior and formation of signaling pathways with iLDQ genes. Future studies may demonstrate the predictive ability of these biomarker genes across other models and additional variables.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2012 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures

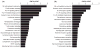
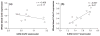

References
-
- Abo-Salem OM, Hayallah AM, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Filipek B, Zimmer A, Muller CE. Antinociceptive effects of novel A2B adenosine receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;308:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Alier KA, Chen Y, Sollenberg UE, Langel U, Smith PA. Selective stimulation of GalR1 and GalR2 in rat substantia gelatinosa reveals a cellular basis for the anti- and pro-nociceptive actions of galanin. Pain. 2008;137:138–146. - PubMed
-
- Andoh T, Kuraishi Y. Direct action of immunoglobulin G on primary sensory neurons through Fc gamma receptor I. FASEB J. 2004a;18:182–184. - PubMed
-
- Andoh T, Kuraishi Y. Expression of Fc epsilon receptor I on primary sensory neurons in mice. Neuro Report. 2004b;15:2029–2031. - PubMed
-
- Austin PJ, Moalem-Taylor G. The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. J Neuroimmunol. 2010;229:26–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

