Development of a comprehensive, validated pharmacophore hypothesis for anthrax toxin lethal factor (LF) inhibitors using genetic algorithms, Pareto scoring, and structural biology
- PMID: 22697455
- PMCID: PMC3477282
- DOI: 10.1021/ci300121p
Development of a comprehensive, validated pharmacophore hypothesis for anthrax toxin lethal factor (LF) inhibitors using genetic algorithms, Pareto scoring, and structural biology
Abstract
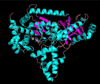
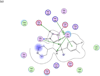
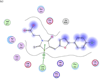
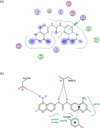
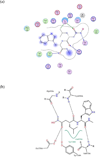
Anthrax is an acute infectious disease caused by the spore-forming bacterium Bacillus anthracis. The anthrax toxin lethal factor (LF), an 89-kDa zinc hydrolase secreted by the bacilli, is the toxin component chiefly responsible for pathogenesis and has been a popular target for rational and structure-based drug design. Although hundreds of small-molecule compounds have been designed to target the LF active site, relatively few reported inhibitors have exhibited activity in cell-based assays, and no LF inhibitor is currently available to treat or prevent anthrax. This study presents a new pharmacophore map assembly, validated by experiment, designed to rapidly identify and prioritize promising LF inhibitor scaffolds from virtual compound libraries. The new hypothesis incorporates structural information from all five available LF enzyme-inhibitor complexes deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) and is the first LF pharmacophore map reported to date that includes features representing interactions involving all three key subsites of the LF catalytic binding region. In a wide-ranging validation study on all 546 compounds for which published LF biological activity data exist, this model displayed strong selectivity toward nanomolar-level LF inhibitors, successfully identifying 72.1% of existing nanomolar-level compounds in an unbiased test set, while rejecting 100% of weakly active (>100 μM) compounds. In addition to its capabilities as a database searching tool, this comprehensive model points to a number of key design principles and previously unidentified ligand-receptor interactions that are likely to influence compound potency.
Figures










References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

