LPS-induced release of IL-6 from glia modulates production of IL-1β in a JAK2-dependent manner
- PMID: 22697788
- PMCID: PMC3418561
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-126
LPS-induced release of IL-6 from glia modulates production of IL-1β in a JAK2-dependent manner
Abstract
Background: Compelling evidence has implicated neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of a number of neurodegenerative conditions. Chronic activation of both astrocytes and microglia leads to excessive secretion of proinflammatory molecules such as TNF α, IL-6 and IL-1 β with potentially deleterious consequences for neuronal viability. Many signaling pathways involving the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), nuclear factor κ B (NF κ B) complex and the Janus kinases (JAKs)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT)-1 have been implicated in the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines from glia. We sought to identify signaling kinases responsible for cytokine production and to delineate the complex interactions which govern time-related responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Methods: We examined the time-related changes in certain signaling events and the release of proinflammatory cytokines from LPS-stimulated co-cultures of astrocytes and microglia isolated from neonatal rats.
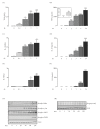
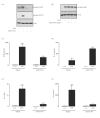
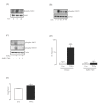
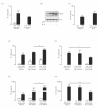
Results: TNF α was detected in the supernatant approximately 1 to 2 hours after LPS treatment while IL-1 β and IL-6 were detected after 2 to 3 and 4 to 6 hours, respectively. Interestingly, activation of NF κ B signaling preceded release of all cytokines while phosphorylation of STAT1 was evident only after 2 hours, indicating that activation of JAK/STAT may be important in the up-regulation of IL-6 production. Additionally, incubation of glia with TNF α induced both phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT1 and the interaction of JAK2 with the TNF α receptor (TNFR1). Co-treatment of glia with LPS and recombinant IL-6 protein attenuated the LPS-induced release of both TNF α and IL-1 β while potentiating the effect of LPS on suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)3 expression and IL-10 release.
Conclusions: These data indicate that TNF α may regulate IL-6 production through activation of JAK/STAT signaling and that the subsequent production of IL-6 may impact on the release of TNF α, IL-1 β and IL-10.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors decrease lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine production in mixed glia, microglia-enriched or astrocyte-enriched cultures.Neurochem Int. 1997 Apr-May;30(4-5):491-7. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(96)00086-1. Neurochem Int. 1997. PMID: 9106265
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 selectively inhibits LPS-induced IL-6 production by regulating JAK-STAT.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 22;102(47):17089-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508517102. Epub 2005 Nov 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16287972 Free PMC article.
-
Mollugin inhibits the inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by blocking the Janus kinase-signal transducers and activators of transcription signaling pathway.Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(3):399-406. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b12-00804. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013. PMID: 23318249
-
GOLD-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC): A Critical Review of Its Properties, Synthesis, and Biomedical Applications.Cureus. 2024 Jan 11;16(1):e52130. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52130. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38344607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcineurin and glial signaling: neuroinflammation and beyond.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Sep 10;11:158. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0158-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 25199950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-TLR2 antibody triggers oxidative phosphorylation in microglia and increases phagocytosis of β-amyloid.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 31;15(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1281-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30170611 Free PMC article.
-
Etanercept alleviates psoriasis by reducing the Th17/Treg ratio and promoting M2 polarization of macrophages.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022 Dec;10(12):e734. doi: 10.1002/iid3.734. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022. PMID: 36444619 Free PMC article.
-
The direct effect of lipopolysaccharide on an isolated heart is different from the effect on cardiac myocytes in vitro.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Aug 2;19(1):216-228. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.86976. eCollection 2023. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 36817673 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocrenatidine Inhibits Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels and Ameliorates Mechanic Allodia in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Apr 18;11(4):229. doi: 10.3390/toxins11040229. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31003411 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimmune mechanisms in autism etiology - untangling a complex problem using human cellular models.Oxf Open Neurosci. 2024 Feb 22;3:kvae003. doi: 10.1093/oons/kvae003. eCollection 2024. Oxf Open Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38665176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cacabelos R, Alvarez XA, Franco-Maside A, Fernandez-Novoa L, Caamano J. Serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1994;16:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Wood JA, Wood PL, Ryan R, Graff-Radford NR, Pilapil C, Robitaille Y, Quirion R. Cytokine indices in Alzheimer’s temporal cortex: no changes in mature IL-1 beta or IL-1RA but increases in the associated acute phase proteins IL-6, alpha 2-macroglobulin and C-reactive protein. Brain Res. 1993;629:245–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91327-O. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

