LPS-induced release of IL-6 from glia modulates production of IL-1β in a JAK2-dependent manner
- PMID: 22697788
- PMCID: PMC3418561
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-126
LPS-induced release of IL-6 from glia modulates production of IL-1β in a JAK2-dependent manner
Abstract
Background: Compelling evidence has implicated neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of a number of neurodegenerative conditions. Chronic activation of both astrocytes and microglia leads to excessive secretion of proinflammatory molecules such as TNF α, IL-6 and IL-1 β with potentially deleterious consequences for neuronal viability. Many signaling pathways involving the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), nuclear factor κ B (NF κ B) complex and the Janus kinases (JAKs)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT)-1 have been implicated in the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines from glia. We sought to identify signaling kinases responsible for cytokine production and to delineate the complex interactions which govern time-related responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Methods: We examined the time-related changes in certain signaling events and the release of proinflammatory cytokines from LPS-stimulated co-cultures of astrocytes and microglia isolated from neonatal rats.
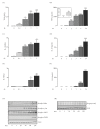
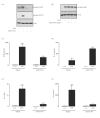
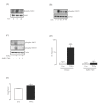
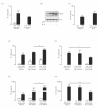
Results: TNF α was detected in the supernatant approximately 1 to 2 hours after LPS treatment while IL-1 β and IL-6 were detected after 2 to 3 and 4 to 6 hours, respectively. Interestingly, activation of NF κ B signaling preceded release of all cytokines while phosphorylation of STAT1 was evident only after 2 hours, indicating that activation of JAK/STAT may be important in the up-regulation of IL-6 production. Additionally, incubation of glia with TNF α induced both phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT1 and the interaction of JAK2 with the TNF α receptor (TNFR1). Co-treatment of glia with LPS and recombinant IL-6 protein attenuated the LPS-induced release of both TNF α and IL-1 β while potentiating the effect of LPS on suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)3 expression and IL-10 release.
Conclusions: These data indicate that TNF α may regulate IL-6 production through activation of JAK/STAT signaling and that the subsequent production of IL-6 may impact on the release of TNF α, IL-1 β and IL-10.
Figures
References
-
- Cacabelos R, Alvarez XA, Franco-Maside A, Fernandez-Novoa L, Caamano J. Serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1994;16:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Wood JA, Wood PL, Ryan R, Graff-Radford NR, Pilapil C, Robitaille Y, Quirion R. Cytokine indices in Alzheimer’s temporal cortex: no changes in mature IL-1 beta or IL-1RA but increases in the associated acute phase proteins IL-6, alpha 2-macroglobulin and C-reactive protein. Brain Res. 1993;629:245–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91327-O. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

