Mincle and human B cell function
- PMID: 22698596
- PMCID: PMC3443704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2012.04.004
Mincle and human B cell function
Abstract
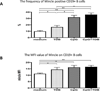
C-type lectin receptors are pattern recognition receptors that are critical for autoimmunity and the immune response. Mincle is a C-type lectin receptor expressed by a variety of antigen presenting cells including macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells and B cells; a variety of stimuli including stress are known to induce the expression of Mincle. Mincle is an FcRγ-associated activation receptor that senses damaged cells and upon ligation induces activated macrophages to produce inflammatory cytokines. Recently, while several studies have reported that Mincle plays an important role in macrophage responses to fungal infection its function on B cells remains to be defined. In efforts to elucidate the function of Mincle expressed by B cells, we studied the expression of Mincle on subsets of B cells and analyzed cytokines and synthesized immunoglobulin upon ligation of Mincle. The expression of Mincle on CD27-CD19(+) naïve B cells is significantly higher than CD27 + CD19(+) memory B cells. The stimulation of TLR9 ligand induced Mincle expression on B cells. Furthermore, co-stimulation of TLR9 and Mincle ligand reduced IgG and IgA production from B cells without a significant change in the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10. Our data identifies Mincle as a potentially critical player in human B cell responses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Matsumoto M, Tanaka T, Kaisho T, Sanjo H, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, et al. A novel LPS-inducible C-type lectin is a transcriptional target of NF-IL6 in macrophages. J Immunol. 1999;163:5039–5048. - PubMed
-
- Zelensky AN, Gready JE. The C-type lectin-like domain superfamily. FEBS J. 2005;272:6179–6217. - PubMed
-
- Yamasaki S, Ishikawa E, Sakuma M, Hara H, Ogata K, Saito T. Mincle is an ITAM-coupled activating receptor that senses damaged cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1179–1188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

