Frey syndrome in neurofibromatosis 1
- PMID: 22698902
- PMCID: PMC3063275
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.09.2009.2286
Frey syndrome in neurofibromatosis 1
Abstract
A healthy 18-month-old girl presented with a history of intermittent hemifacial flushing when eating. Her symptom seemed to be exclusively triggered by chewing. Examination revealed cutaneous features of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and mild facial asymmetry. Imaging confirmed cerebral vacuolisation changes seen in NF1 and a left facial plexiform neurofibroma involving the parotid gland. This is the first reported case of Frey syndrome complicating NF1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

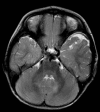
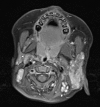
References
-
- Frey L. Le syndrome de nerf auriculotemporal. Rev Neurol 1923;2:97–9
-
- Moore KL, Agur AMR. Essential Clinical Anatomy. Third Edition Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007:691
-
- Luna Ortiz K, Rascon Ortiz M, Sansón Riofrio JA, et al. Control of Frey’s Syndrome in Patients Treated with Botulinum Type A. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2007;12:E79–84 - PubMed
-
- O’Neill JP, Condron C, Curran A, et al. Lucja Frey–historical relevance and syndrome review. Surgeon 2008;6:178–81 - PubMed
-
- Dizon MV, Fischer G, Jopp-McKay A, et al. Localized facial flushing in infancy. Auriculotemporal nerve (Frey) syndrome. Arch Dermatol 1997;133:1143–5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
