Autoantigen-specific B-cell depletion overcomes failed immune tolerance in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 22698916
- PMCID: PMC3402296
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1746
Autoantigen-specific B-cell depletion overcomes failed immune tolerance in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
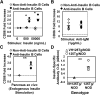
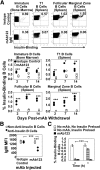
Eliminating autoantigen-specific B cells is an attractive alternative to global B-cell depletion for autoimmune disease treatment. To identify the potential for targeting a key autoimmune B-cell specificity in type 1 diabetes, insulin-binding B cells were tracked within a polyclonal repertoire using heavy chain B-cell receptor (BCR) transgenic (VH125Tg) mice. Insulin-specific B cells are rare in the periphery of nonautoimmune VH125Tg/C57BL/6 mice and WT/NOD autoimmune mice, whereas they clearly populate 1% of mature B-cell subsets in VH125Tg/NOD mice. Autoantigen upregulates CD86 in anti-insulin B cells, suggesting they are competent to interact with T cells. Endogenous insulin occupies anti-insulin BCR beginning with antigen commitment in bone marrow parenchyma, as identified by a second anti-insulin monoclonal antibody. Administration of this monoclonal antibody selectively eliminates insulin-reactive B cells in vivo and prevents disease in WT/NOD mice. Unexpectedly, developing B cells are less amenable to depletion, despite increased BCR sensitivity. These findings exemplify how a critical type 1 diabetes B-cell specificity escapes immune tolerance checkpoints. Disease liability is corrected by eliminating this B-cell specificity, providing proof of concept for a novel therapeutic approach for autoimmune disease.
Figures



References
-
- Hulbert C, Riseili B, Rojas M, Thomas JW. B cell specificity contributes to the outcome of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol 2001;167:5535–5538 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-DK-08246/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051448/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-051448/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32-HL-069765/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084246/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32-AR-059039/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR059039/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069765/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

