Metformin inhibits growth hormone-mediated hepatic PDK4 gene expression through induction of orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner
- PMID: 22698918
- PMCID: PMC3447904
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1665
Metformin inhibits growth hormone-mediated hepatic PDK4 gene expression through induction of orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner
Abstract
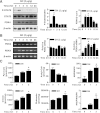
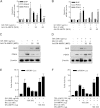
Growth hormone (GH) is a counter-regulatory hormone that plays an important role in preventing hypoglycemia during fasting. Because inhibition of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) conserves substrates for gluconeogenesis, we tested whether GH increases PDK4 expression in liver by a signaling pathway sensitive to inhibition by metformin. The effects of GH and metformin were determined in the liver of wild-type, small heterodimer partner (SHP)-, PDK4-, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5)-null mice. Administration of GH in vivo increased PDK4 expression via a pathway dependent on STAT5 phosphorylation. Metformin inhibited the induction of PDK4 expression by GH via a pathway dependent on AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and SHP induction. The increase in PDK4 expression and PDC phosphorylation by GH was reduced in STAT5-null mice. Metformin decreased GH-mediated induction of PDK4 expression and metabolites in wild-type but not in SHP-null mice. In primary hepatocytes, dominant-negative mutant-AMPK and SHP knockdown prevented the inhibitory effect of metformin on GH-stimulated PDK4 expression. SHP directly inhibited STAT5 association on the PDK4 gene promoter. Metformin inhibits GH-induced PDK4 expression and metabolites via an AMPK-SHP-dependent pathway. The metformin-AMPK-SHP network may provide a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of hepatic metabolic disorders induced by the GH-mediated pathway.
Figures




References
-
- White MF. Metformin and insulin meet in a most atypical way. Cell Metab 2009;9:485–487 - PubMed
-
- Edgerton DS, Johnson KM, Cherrington AD. Current strategies for the inhibition of hepatic glucose production in type 2 diabetes. Front Biosci 2009;14:1169–1181 - PubMed
-
- Zhang BB, Zhou G, Li C. AMPK: an emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 2009;9:407–416 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

