The let-7 microRNA enhances heme oxygenase-1 by suppressing Bach1 and attenuates oxidant injury in human hepatocytes
- PMID: 22698995
- PMCID: PMC3480558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.06.001
The let-7 microRNA enhances heme oxygenase-1 by suppressing Bach1 and attenuates oxidant injury in human hepatocytes
Abstract
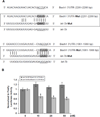
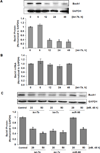
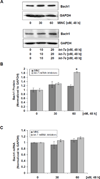
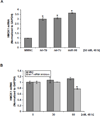
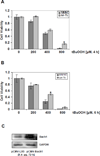
The let-7 microRNA (miRNA) plays important roles in human liver development and diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma, liver fibrosis and hepatitis wherein oxidative stress accelerates the progression of these diseases. To date, the role of the let-7 miRNA family in modulation of heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1), a key cytoprotective enzyme, remains unknown. Our aims were to determine whether let-7 miRNA directly regulates Bach1, a transcriptional repressor of the HMOX1 gene, and whether indirect up-regulation of HMOX1 by let-7 miRNA attenuates oxidant injury in human hepatocytes. The effects of let-7 miRNA on Bach1 and HMOX1 gene expression in Huh-7 and HepG2 cells were determined by real-time qRT-PCR, Western blot, and luciferase reporter assays. Dual luciferase reporter assays revealed that let-7b, let-7c, or miR-98 significantly decreased Bach1 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR)-dependent luciferase activity but not mutant Bach1 3'-UTR-dependent luciferase activity, whereas mutant let-7 miRNA containing base complementarity with mutant Bach1 3'-UTR restored its effect on mutant reporter activity. let-7b, let-7c, or miR-98 down-regulated Bach1 protein levels by 50-70%, and subsequently up-regulated HMOX1 gene expression by 3-4 fold, compared with non-specific controls. Furthermore, Huh-7 cells transfected with let-7b, let-7c or miR-98 mimic showed increased resistance against oxidant injury induced by tert-butyl-hydroperoxide (tBuOOH), whereas the protection was abrogated by over-expression of Bach1. In conclusion, let-7 miRNA directly acts on the 3'-UTR of Bach1 and negatively regulates expression of this protein, and thereby up-regulates HMOX1 gene expression. Over-expression of the let-7 miRNA family members may represent a novel approach to protecting human hepatocytes from oxidant injury.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Elbirt KK, Bonkovsky HL. Heme oxygenase: recent advances in understanding its regulation and role. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999;111:438–447. - PubMed
-
- Bonkovsky HL, Elbirt KK. Heme Oxygenase: Its Regulation and Role. In: Cutler RG, Rodriguez H, editors. Oxidative Stress and Aging, World Scientific. River Edge, NJ: 2002. pp. 699–706.
-
- Brugger J, Schick MA, Brock RW, Baumann A, Muellenbach RM, Roewer N, Wunder C. Carbon monoxide has antioxidative properties in the liver involving p38 MAP kinase pathway in a murine model of systemic inflammation. Microcirculation. 2010;17:504–513. - PubMed
-
- Wu TW, Carey D, Wu J, Sugiyama H. The cytoprotective effects of bilirubin and biliverdin on rat hepatocytes and human erythrocytes and the impact of albumin. Biochemistry and cell biology. 1991;69:828–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

