Separate and combined effects of the GABA(B) agonist baclofen and Δ9-THC in humans discriminating Δ9-THC
- PMID: 22699093
- PMCID: PMC3478434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.05.023
Separate and combined effects of the GABA(B) agonist baclofen and Δ9-THC in humans discriminating Δ9-THC
Abstract
Background: Our previous research with the GABA reuptake inhibitor tiagabine suggested the involvement GABA in the interoceptive effects of Δ9-THC. The aim of the present study was to determine the potential involvement of the GABA(B) receptor subtype by assessing the separate and combined effects of the GABA(B)-selective agonist baclofen and Δ9-THC using pharmacologically specific drug-discrimination procedures.
Methods: Eight cannabis users learned to discriminate 30 mg oral Δ9-THC from placebo and then received baclofen (25 and 50mg), Δ9-THC (5, 15 and 30 mg) and placebo, alone and in combination. Self-report, task performance and physiological measures were also collected.
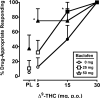
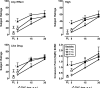
Results: Δ9-THC functioned as a discriminative stimulus, produced subjective effects typically associated with cannabinoids (e.g., High, Stoned, Like Drug), elevated heart rate and impaired rate and accuracy on a psychomotor performance task. Baclofen alone (50 mg) substituted for the Δ9-THC discriminative stimulus, and both baclofen doses shifted the discriminative-stimulus effects of Δ9-THC leftward/upward. Similar results were observed on other cannabinoid-sensitive outcomes, although baclofen generally did not engender Δ9-THC-like subjective responses when administered alone.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the GABA(B) receptor subtype is involved in the abuse-related effects of Δ9-THC, and that GABA(B) receptors were responsible, at least in part, for the effects of tiagabine-induced elevated GABA on cannabinoid-related behaviors in our previous study. Future research should test GABAergic compounds selective for other GABA receptor subtypes (i.e., GABA(A)) to determine the contribution of the different GABA receptors in the effects of Δ9-THC, and by extension cannabis, in humans.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
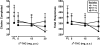

References
-
- Baclofen Product Information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Limited; 2008.
-
- Browne RG, Weissman A. Discriminative stimulus properties of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol: mechanistic studies. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981;21:S227–34. - PubMed
-
- Castellano C, Rossi-Arnaud C, Cestari V, Costanzi M. Cannabinoids and memory: animal studies. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2003;2:389–402. - PubMed
-
- Cousins MS, Stamat MS, de Wit H. Effects of a single dose of baclofen on self-reported subjective effects and tobacco smoking. Nicotine Tob. Res. May. 2001;3:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Dario A, Pisani R, Sangiorgi S, Pessina F, Tomei G. Relationship between intrathecal baclofen and the central nervous system. Acta. Neurochir. Suppl. 2007;97:461–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

