A single ligand is sufficient to activate EGFR dimers
- PMID: 22699492
- PMCID: PMC3390854
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1201114109
A single ligand is sufficient to activate EGFR dimers
Abstract
Crystal structures of human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with bound ligand revealed symmetric, doubly ligated receptor dimers thought to represent physiologically active states. Such complexes fail to rationalize negative cooperativity of epidermal growth factor (EGF) binding to EGFR and the behavior of the ligandless EGFR homolog ErbB2/HER2, however. We report cell-based assays that provide evidence for active, singly ligated dimers of human EGFR and its homolog, ErbB4/HER4. We also report crystal structures of the ErbB4/HER4 extracellular region complexed with its ligand Neuregulin-1β that resolve two types of ErbB dimer when compared to EGFR:Ligand complexes. One type resembles the recently reported asymmetric dimer of Drosophila EGFR with a single high-affinity ligand bound and provides a model for singly ligated human ErbB dimers. These results unify models of vertebrate and invertebrate EGFR/ErbB signaling, imply that the tethered conformation of unliganded ErbBs evolved to prevent crosstalk among ErbBs, and establish a molecular basis for both negative cooperativity of ligand binding to vertebrate ErbBs and the absence of active ErbB2/HER2 homodimers in normal conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
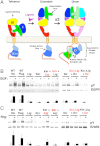
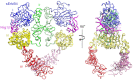
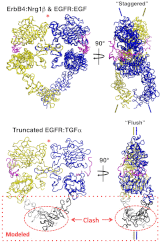
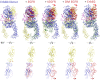
References
-
- Burgess AW. EGFR family: Structure physiology signalling and therapeutic targets. Growth Factors. 2008;26:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Heldin CH. Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction. Cell. 1995;80:213–223. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y, Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987;26:1443–1451. - PubMed
-
- Burgess AW, et al. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol Cell. 2003;12:541–552. - PubMed
-
- Chung I, et al. Spatial control of EGF receptor activation by reversible dimerization on living cells. Nature. 2010;464(7289):783–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

