Common variation at 6p21.31 (BAK1) influences the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 22700719
- PMCID: PMC3412347
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-413591
Common variation at 6p21.31 (BAK1) influences the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
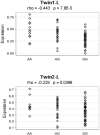
We performed a meta-analysis of 3 genome-wide association studies to identify additional common variants influencing chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) risk. The discovery phase was composed of genome-wide association study data from 1121 cases and 3745 controls. Replication analysis was performed in 861 cases and 2033 controls. We identified a novel CLL risk locus at 6p21.33 (rs210142; intronic to the BAK1 gene, BCL2 antagonist killer 1; P = 9.47 × 10(-16)). A strong relationship between risk genotype and reduced BAK1 expression was shown in lymphoblastoid cell lines. This finding provides additional support for polygenic inheritance to CLL and provides further insight into the biologic basis of disease development.
Figures
References
-
- Stevenson FK, Caligaris-Cappio F. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revelations from the B-cell receptor. Blood. 2004;103(12):4389–4395. - PubMed
-
- Goldin LR, Pfeiffer RM, Li X, Hemminki K. Familial risk of lymphoproliferative tumors in families of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from the Swedish Family-Cancer Database. Blood. 2004;104(6):1850–1854. - PubMed
-
- Di Bernardo MC, Crowther-Swanepoel D, Broderick P, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies six susceptibility loci for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2008;40(10):1204–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA118444/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA89745/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA154643-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA148690/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148690/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA92153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA122663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA104682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154643/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA134919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R03 CA089745/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K08CA134919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045614/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201000026C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1298/A8362/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA118444/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

