Discovering the bacterial circular proteins: bacteriocins, cyanobactins, and pilins
- PMID: 22700986
- PMCID: PMC3411037
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R112.354688
Discovering the bacterial circular proteins: bacteriocins, cyanobactins, and pilins
Abstract
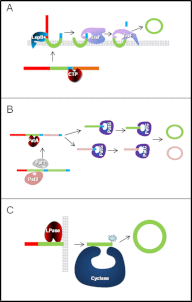
Over recent years, several examples of natural ribosomally synthesized circular proteins and peptides from diverse organisms have been described. They are a group of proteins for which the precursors must be post-translationally modified to join the N and C termini with a peptide bond. This feature appears to confer a range of potential advantages because these proteins show increased resistance to proteases and higher thermodynamic stability, both of which improve their biological activity. They are produced by prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms and show diverse biological activities, related mostly to a self-defense or competition mechanism of the producer organisms, with the only exception being the circular pilins. This minireview highlights ribosomally synthesized circular proteins produced by members of the domain Bacteria: circular bacteriocins, cyanobactins, and circular pilins. We pay special attention to the genetic organization of the biosynthetic machinery of these molecules, the role of circularization, and the differences in the possible circularization mechanisms.
Figures

References
-
- Maqueda M., Sánchez-Hidalgo M., Fernández M., Montalbán-López M., Valdivia E., Martínez-Bueno M. (2008) Genetic features of circular bacteriocins produced by Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 32, 2–22 - PubMed
-
- Martin-Visscher L. A., van Belkum M. J., Vederas J. C. (2011) in Prokaryotic Antimicrobial Peptides: From Genes to Application (Drider D., Rebuffat S., eds) pp. 213–236, Springer, Heidelberg
-
- Conlan B. F., Gillon A. D., Craik D. J., Anderson M. A. (2010) Circular proteins and mechanisms of cyclization. Biopolymers 94, 573–583 - PubMed
-
- van Belkum M. J., Martin-Visscher L. A., Vederas J. C. (2011) Structure and genetics of circular bacteriocins. Trends Microbiol. 19, 411–418 - PubMed
-
- Kawai Y., Kemperman R., Kok J., Saito T. (2004) The circular bacteriocins gassericin A and circularin A. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 5, 393–398 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

