Pilot study of oral administration of a curcumin-phospholipid formulation for treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy
- PMID: 22701080
- PMCID: PMC3373230
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S31859
Pilot study of oral administration of a curcumin-phospholipid formulation for treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this open-label study was to investigate the effect of a curcumin-phospholipid (lecithin, Meriva(®)) formulation (Norflo(®) tablet) on visual acuity and retinal thickness in patients with acute or chronic central serous chorioretinopathy.
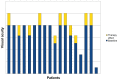
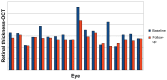
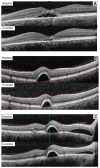
Methods: Visual acuity was assessed by ophthalmologic evaluation, and optical coherence tomography was used to measure retinal thickness. Norflo tablets were administered twice a day to patients affected by central serous chorioretinopathy. The study included 18 eyes from 12 patients who completed a 6-month follow-up period. Visual acuity before and after Norflo treatment was the primary endpoint. The secondary endpoints were neuroretinal or pigment epithelial detachment, as measured by optical coherence tomography.
Results: After 6 months of therapy, 0% of eyes showed reduction in visual acuity, 39% showed stabilization, and 61% showed improvement. The improvement was statistically significant (P = 0.08). After 6 months of therapy, 78% of eyes showed reduction of neuroretinal or retinal pigment epithelium detachment, 11% showed stabilization, and 11% showed an increase.
Conclusion: Our results, albeit preliminary, show that curcumin administered as Norflo tablets is efficacious for the management of central serous chorioretinopathy, a relapsing eye disease, and suggest that bioavailable curcumin is worth considering as a therapeutic agent for the management of inflammatory and degenerative eye conditions, including those that activate the retinal microglia.
Keywords: Meriva®; Norflo®; central serous chorioretinopathy; curcumin; retinal pigment epithelium detachment.
Figures
References
-
- Graefe AV. Uber centrale recidivierende retinitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1866;12:211–215. [German]
-
- Gass JD. Pathogenesis of disciform detachment of the neuroepithelium. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967;63(Suppl 3):1–139. - PubMed
-
- Mohan R, Sivak J, Ashton P, et al. Curcuminoids inhibit the angiogenic response stimulated by fibroblast growth factor-2, including expression of matrix metalloproteinase gelatinase B. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(14):10405–10412. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Hu DN, Pan Z, Lu CW, Xue CY, Aass I. Curcumin protects against hyperosmoticity-induced IL-1 beta elevation in human corneal epithelial cell via MAPK pathways. Exp Eye Res. 2010;90(3):437–443. - PubMed
-
- Bengmark S. Curcumin, an atoxic antioxidant and natural NF kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, lipooxygenase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor: a shield against acute and chronic diseases. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2006;30(1):45–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

