The Poor Survival among Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients in Chiapas, Mexico: The Case of Los Altos Region
- PMID: 22701170
- PMCID: PMC3369422
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/708423
The Poor Survival among Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients in Chiapas, Mexico: The Case of Los Altos Region
Abstract
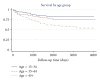
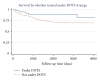
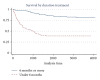
Objective. To analyse survival in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) and factors associated with such survival. Design. Study of a cohort of patients aged over 14 years diagnosed with PTB from January 1, 1998 to July 31, 2005. During 2004-2006 a home visit was made to each patient and, during 2008-2009, they were visited again. During these visits a follow-up interview was administered; when the patient had died, a verbal autopsy was conducted with family members. Statistical analysis consisted of survival tests, Kaplan-Meier log-rank test and Cox regression. Results. Of 305 studied patients, 68 had died due to PTB by the time of the first evaluation, 237 were followed-up for a second evaluation, and 10 of them had died of PTB. According to the Cox regression, age (over 45 years) and treatment duration (under six months) were associated with a poorer survival. When treatment duration was excluded, the association between poorer survival with age persisted, whereas with having been treated via DOTS strategy, was barely significant. Conclusions. In the studied area it is necessary that patients receive a complete treatment scheme, and to give priority to patients aged over 45 years.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Demographic, health services and socio-economic factors associated with pulmonary tuberculosis mortality in Los Altos Region of Chiapas, Mexico.Int J Epidemiol. 2008 Aug;37(4):786-95. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn089. Epub 2008 May 29. Int J Epidemiol. 2008. PMID: 18511492
-
Anti-tuberculosis treatment defaulting: an analysis of perceptions and interactions in Chiapas, Mexico.Salud Publica Mex. 2008 May-Jun;50(3):251-7. doi: 10.1590/s0036-36342008000300009. Salud Publica Mex. 2008. PMID: 18516373
-
Multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in Los Altos, Selva and Norte regions, Chiapas, Mexico.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010 Jan;14(1):34-9. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010. PMID: 20003692
-
Pulmonary tuberculosis and associated factors in areas of high levels of poverty in Chiapas, Mexico.Int J Epidemiol. 2001 Apr;30(2):386-93. doi: 10.1093/ije/30.2.386. Int J Epidemiol. 2001. PMID: 11369747
-
Imaging modalities for pulmonary tuberculosis in children: A systematic review.Eur J Radiol Open. 2022 Dec 30;10:100472. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2022.100472. eCollection 2023. Eur J Radiol Open. 2022. PMID: 36624819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetes, undernutrition, migration and indigenous communities: tuberculosis in Chiapas, Mexico.Epidemiol Infect. 2019 Jan;147:e71. doi: 10.1017/S0950268818003461. Epidemiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 30869023 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Biosensing Assay Quantitatively Enhances Acid-Fast Bacilli Count in Paucibacillary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.Biosensors (Basel). 2018 Dec 12;8(4):128. doi: 10.3390/bios8040128. Biosensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30545099 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates From an Amerindian Population in Chiapas, México.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 13;12:875909. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.875909. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35909960 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and Predictors of Death after Successful Treatment among Smear Positive Tuberculosis: A Cohort Study.Int J Prev Med. 2014 Aug;5(8):1005-12. Int J Prev Med. 2014. PMID: 25489449 Free PMC article.
-
Haematophagous bat bites in Ecuadorian Amazon: characterisation and implications for sylvatic rabies prevention.Public Health Action. 2013 Mar 21;3(1):85-9. doi: 10.5588/pha.12.0070. Public Health Action. 2013. PMID: 26393003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Health Organization World. An Expanded DOTS Framework for Effective Tuberculosis Control. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO/CDS/TB/2002.297; 2002.
-
- Health Organization World. Global Tuberculosis Control. Epidemiology, Strategy, Financing. Ginebra, Switzerland: WHO/HTM/TB/2009.411; 2009.
-
- de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos, Presidencia de la República Gobierno. Plan Nacional de Desarrollo 2007-2012. México, D.F., 2007.
-
- for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Organisation. OECD Reviews of Health Systems: MEXICO. Paris, France: OECD; 2005.
-
- General de Información en Salud Dirección. Sistema de Cuentas Nacionales y Estatales de Salud (SICUENTAS), Secretaría de Salud, México. Estadísticas de recursos financieros públicos para la salud en México, 2003. Salud Publica Mex. 2005;47:90–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources