A new piezoelectric actuator induces bone formation in vivo: a preliminary study
- PMID: 22701304
- PMCID: PMC3369535
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/613403
A new piezoelectric actuator induces bone formation in vivo: a preliminary study
Abstract
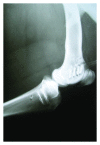
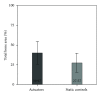
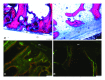
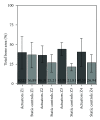
This in vivo study presents the preliminary results of the use of a novel piezoelectric actuator for orthopedic application. The innovative use of the converse piezoelectric effect to mechanically stimulate bone was achieved with polyvinylidene fluoride actuators implanted in osteotomy cuts in sheep femur and tibia. The biological response around the osteotomies was assessed through histology and histomorphometry in nondecalcified sections and histochemistry and immunohistochemistry in decalcified sections, namely, through Masson's trichrome, and labeling of osteopontin, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. After one-month implantation, total bone area and new bone area were significantly higher around actuators when compared to static controls. Bone deposition rate was also significantly higher in the mechanically stimulated areas. In these areas, osteopontin increased expression was observed. The present in vivo study suggests that piezoelectric materials and the converse piezoelectric effect may be used to effectively stimulate bone growth.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhancement of Bone Regeneration Through the Converse Piezoelectric Effect, A Novel Approach for Applying Mechanical Stimulation.Bioelectricity. 2021 Dec 1;3(4):255-271. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2021.0019. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Bioelectricity. 2021. PMID: 35018335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteogenesis and morphology of the peri-implant bone facing dental implants.ScientificWorldJournal. 2004 Dec 14;4:1083-95. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2004.211. ScientificWorldJournal. 2004. PMID: 15632988 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-Forming Effect of a Static Magnetic Field in Rabbit Femurs.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2019 Mar/Apr;39(2):259-264. doi: 10.11607/prd.3220. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2019. PMID: 30794262
-
Dose-dependent new bone formation by extracorporeal shock wave application on the intact femur of rabbits.Eur Surg Res. 2008;41(1):44-53. doi: 10.1159/000128279. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Eur Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 18441525
-
Lower limb lengthening by a modified Wagner technique.J Pediatr Orthop. 1989 Mar-Apr;9(2):129-33. J Pediatr Orthop. 1989. PMID: 2647783 Review.
Cited by
-
POLYMERIC BIOMATERIALS FOR SCAFFOLD-BASED BONE REGENERATIVE ENGINEERING.Regen Eng Transl Med. 2019 Jun;5(2):128-154. doi: 10.1007/s40883-018-0072-0. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31423461 Free PMC article.
-
Electrically Active Biomaterials for Stimulation and Regeneration in Tissue Engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2025 Jan;113(1):e37871. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37871. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2025. PMID: 39806919 Review.
-
Sensor Technology in Fracture Healing.Indian J Orthop. 2023 Jun 23;57(8):1196-1202. doi: 10.1007/s43465-023-00933-3. eCollection 2023 Aug. Indian J Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37525725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of Bone Regeneration Through the Converse Piezoelectric Effect, A Novel Approach for Applying Mechanical Stimulation.Bioelectricity. 2021 Dec 1;3(4):255-271. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2021.0019. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Bioelectricity. 2021. PMID: 35018335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioelectronic multifunctional bone implants: recent trends.Bioelectron Med. 2022 Sep 21;8(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s42234-022-00097-9. Bioelectron Med. 2022. PMID: 36127721 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewandowska-Szumieł M, Sikorski K, Szummer A, Lewandowski Z, Marczyński W. Osteoblast response to the elastic strain of metallic support. Journal of Biomechanics. 2007;40(3):554–560. - PubMed
-
- Kadow-Romacker A, Hoffmann JE, Duda G, Wildemann B, Schmidmaier G. Effect of mechanical stimulation on osteoblast- and osteoclast-like cells in vitro. Cells Tissues Organs. 2009;190(2):61–68. - PubMed
-
- Rubin CT, Lanyon LE. Regulation of bone formation by applied dynamic loads. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery A. 1984;66(3):397–402. - PubMed
-
- Bourrin S, Palle S, Pupier R, Vico L, Alexandre C. Effects of physical training on bone adaptation in three zones of the rat tibia. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 1995;10(11):1745–1752. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh Y-F, Turner CH. Effects of loading frequency on mechanically induced bone formation. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2001;16(5):918–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

