A native plant growth promoting bacterium, Bacillus sp. B55, rescues growth performance of an ethylene-insensitive plant genotype in nature
- PMID: 22701461
- PMCID: PMC3371617
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00112
A native plant growth promoting bacterium, Bacillus sp. B55, rescues growth performance of an ethylene-insensitive plant genotype in nature
Abstract
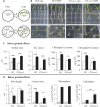
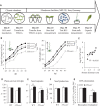
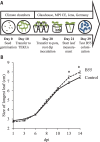
Many plants have intimate relationships with soil microbes, which improve the plant's growth and fitness through a variety of mechanisms. Bacillus sp. isolates are natural root-associated bacteria, isolated from Nicotiana attenuata plant roots growing in native soils. A particular isolate B55, was found to have dramatic plant growth promotion (PGP) effects on wild type (WT) and transgenic plants impaired in ethylene (ET) perception (35S-etr1), the genotype from which this bacterium was first isolated. B55 not only improves N. attenuata growth under in vitro, glasshouse, and field conditions, but it also "rescues" many of the deleterious phenotypes associated with ET insensitivity. Most notably, B55 dramatically increases the growth and survival of 35S-etr1 plants under field conditions. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of a PGP effect in a native plant-microbe association under natural conditions. Our study demonstrates that this facultative mutualistic plant-microbe interaction should be viewed as part of the plant's extended phenotype. Possible modalities of recruitment and mechanisms of PGP are discussed.
Keywords: Bacillus sp.; Nicotiana attenuata; ethylene-insensitive; extended phenotype; microbial community; nature; plant growth promotion.
Figures
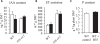

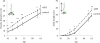
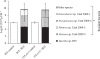
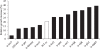
Similar articles
-
Dimethyl disulfide produced by the naturally associated bacterium bacillus sp B55 promotes Nicotiana attenuata growth by enhancing sulfur nutrition.Plant Cell. 2013 Jul;25(7):2731-47. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.114744. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23903320 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of the culturable root bacterial endophyte community of Nicotiana attenuata is organized by soil composition and host plant ethylene production and perception.New Phytol. 2010 Jan;185(2):554-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03079.x. Epub 2009 Nov 10. New Phytol. 2010. PMID: 19906091
-
Symbiosis between Nicotiana attenuata and Glomus intraradices: ethylene plays a role, jasmonic acid does not.Plant Cell Environ. 2008 Sep;31(9):1203-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01827.x. Epub 2008 May 23. Plant Cell Environ. 2008. PMID: 18507809
-
Alleviation of Heavy Metal Stress in Plants and Remediation of Soil by Rhizosphere Microorganisms.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 6;8:1706. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01706. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28932218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in microbe-assisted reclamation of heavy metal contaminated soils over the last decade: A review.J Environ Manage. 2017 Aug 1;198(Pt 1):132-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.060. Epub 2017 Apr 26. J Environ Manage. 2017. PMID: 28456029 Review.
Cited by
-
Volatile organic compounds emitted by Burkholderia pyrrocinia CNUC9 trigger induced systemic salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1050901. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1050901. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36466674 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Draft Genome Sequence of Bacillus sp. Strain YF23, Which Has Plant Growth-Promoting Activity.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019 Apr 11;8(15):e00099-19. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00099-19. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019. PMID: 30975803 Free PMC article.
-
In wild tobacco, Nicotiana attenuata, variation among bacterial communities of isogenic plants is mainly shaped by the local soil microbiota independently of the plants' capacity to produce jasmonic acid.Commun Integr Biol. 2015 May 1;8(2):e1017160. doi: 10.1080/19420889.2015.1017160. eCollection 2015 Mar-Apr. Commun Integr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26478769 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Sequencing of Rahnella victoriana JZ-GX1 Provides New Insights Into Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of Plant Growth Promotion.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 30;13:828990. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.828990. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35464970 Free PMC article.
-
Metatranscriptomics and Amplicon Sequencing Reveal Mutualisms in Seagrass Microbiomes.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 15;9:388. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00388. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29599758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aeron A., Kumar S., Pandey P., Maheshwari D. K. (2011). “Emerging role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agrobiology,” in Bacteria in Agrobiology: Crop Ecosystems ed. Maheshwari D. K. (Berlin: Springer; ), 1–36
-
- Allmann S., Halitschke R., Schuurink R. C., Baldwin I. T. (2010). Oxylipin channelling in Nicotiana attenuata: lipoxygenase 2 supplies substrates for green leaf volatile production. Plant Cell Environ. 33 2028–2040 - PubMed
-
- Barazani O., Benderoth M., Groten K., Kuhlemeier C., Baldwin I. T. (2005). Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera increase growth performance at the expense of herbivore resistance in Nicotiana attenuata. Oecologia 146 234–243 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

