Heme degrading protein HemS is involved in oxidative stress response of Bartonella henselae
- PMID: 22701524
- PMCID: PMC3365110
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037630
Heme degrading protein HemS is involved in oxidative stress response of Bartonella henselae
Abstract
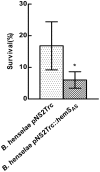
Bartonellae are hemotropic bacteria, agents of emerging zoonoses. These bacteria are heme auxotroph Alphaproteobacteria which must import heme for supporting their growth, as they cannot synthesize it. Therefore, Bartonella genome encodes for a complete heme uptake system allowing the transportation of this compound across the outer membrane, the periplasm and the inner membranes. Heme has been proposed to be used as an iron source for Bartonella since these bacteria do not synthesize a complete system required for iron Fe³⁺ uptake. Similarly to other bacteria which use heme as an iron source, Bartonellae must transport this compound into the cytoplasm and degrade it to allow the release of iron from the tetrapyrrole ring. For Bartonella, the gene cluster devoted to the synthesis of the complete heme uptake system also contains a gene encoding for a polypeptide that shares homologies with heme trafficking or degrading enzymes. Using complementation of an E. coli mutant strain impaired in heme degradation, we demonstrated that HemS from Bartonella henselae expressed in E. coli allows the release of iron from heme. Purified HemS from B. henselae binds heme and can degrade it in the presence of a suitable electron donor, ascorbate or NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Knocking down the expression of HemS in B. henselae reduces its ability to face H₂O₂ induced oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Heme binding proteins of Bartonella henselae are required when undergoing oxidative stress during cell and flea invasion.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048408. Epub 2012 Oct 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144761 Free PMC article.
-
Managing iron supply during the infection cycle of a flea borne pathogen, Bartonella henselae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Oct 18;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00060. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24151576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemin binding protein C is found in outer membrane vesicles and protects Bartonella henselae against toxic concentrations of hemin.Infect Immun. 2012 Mar;80(3):929-42. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05769-11. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22232189 Free PMC article.
-
The Bartonella henselae SitABCD transporter is required for confronting oxidative stress during cell and flea invasion.Res Microbiol. 2013 Oct;164(8):827-37. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Res Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23811032
-
[Prevalence of Bartonella henselae in stray and domestic cats in different Italian areas: evaluation of the potential risk of transmission of Bartonella to humans].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):127-9. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305701 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
The Detection of Hemin-Binding Proteins in Riemerella anatipestifer CH-1.Curr Microbiol. 2016 Feb;72(2):152-158. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0932-5. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Curr Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26542531
-
Iron homeostasis in the Rhodobacter genus.Adv Bot Res. 2013;66:10.1016/B978-0-12-397923-0.00010-2. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397923-0.00010-2. Adv Bot Res. 2013. PMID: 24382933 Free PMC article.
-
From Host Heme To Iron: The Expanding Spectrum of Heme Degrading Enzymes Used by Pathogenic Bacteria.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 19;8:198. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00198. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29971218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights from a Genome-Wide Study of Pantoea agglomerans UADEC20: A Promising Strain for Phosphate Solubilization and Exopolysaccharides Production.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 16;47(1):56. doi: 10.3390/cimb47010056. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39852170 Free PMC article.
-
Heme binding proteins of Bartonella henselae are required when undergoing oxidative stress during cell and flea invasion.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048408. Epub 2012 Oct 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breitschwerdt EB, Maggi RG, Chomel BB, Lappin MR. Bartonellosis: an emerging infectious disease of zoonotic importance to animals and human beings. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio) 2010;20:8–30. - PubMed
-
- Guptill L. Bartonellosis. Vet Microbiol. 2010;140:347–359. - PubMed
-
- Edouard S, Raoult D. Bartonella henselae, an ubiquitous agent of proteiform zoonotic disease. Med Mal Infect. 2010;40:319–330. - PubMed
-
- Klotz SA, Ianas V, Elliott SP. Cat-scratch Disease. Am Fam Physician. 2011;83:152–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

