Circulating DNA: diagnostic tool and predictive marker for overall survival of NSCLC patients
- PMID: 22701665
- PMCID: PMC3373551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038559
Circulating DNA: diagnostic tool and predictive marker for overall survival of NSCLC patients
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of our study was to determine whether the amounts of circulating DNA (cDNA) could discriminate between NSCLC patients and healthy individuals and assess its value as a prognostic marker of this disease.
Methods: We conducted a study of 309 individuals and the cDNA levels were assessed through real-time PCR methodology.
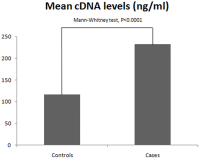
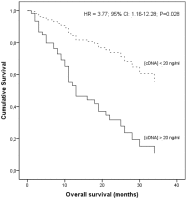
Results: We found increased cDNA levels in NSCLC patients compared to control individuals. We also found a decreased overall survival time in patients presenting high cDNA levels, when compared to lower cDNA concentrations.
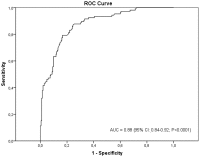
Conclusions: Quantification of cDNA may be a good tool for NSCLC detection with potential for clinical applicability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Paci M, Maramotti S, Bellesia E, Formisano D, Albertazzi L, et al. Circulating plasma DNA as diagnostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2009;64:92–97. - PubMed
-
- Brundage MD, Davies D, Mackillop WJ. Prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer: a decade of progress. Chest. 2002;122:1037–1057. - PubMed
-
- Wakelee HA, Bernardo P, Johnson DH, Schiller JH. Changes in the natural history of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC)–comparison of outcomes and characteristics in patients with advanced NSCLC entered in Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trials before and after 1990. Cancer. 2006;106:2208–2217. - PubMed
-
- de Geus-Oei LF, van der Heijden HF, Corstens FH, Oyen WJ. Predictive and prognostic value of FDG-PET in nonsmall-cell lung cancer: a systematic review. Cancer. 2007;110:1654–1664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

