HHV-6B induces IFN-lambda1 responses in cord plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR9
- PMID: 22701693
- PMCID: PMC3368904
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038683
HHV-6B induces IFN-lambda1 responses in cord plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR9
Abstract
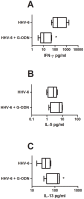
Human herpesvirus type 6B (HHV-6B) is a strong inducer of IFN-alpha and has the capacity to promote Th1 responses and block Th2 responses in vitro. In this study we addressed whether inactivated HHV-6B can also induce IFN lambda responses and to what extent interferons alpha and lambda affect Th1/Th2 polarization. We show that inactivated HHV-6B induced IFN-lambda1 (IL-29) but not IFN-lambda2 (IL-28A) responses in plasmacytoid DC and that this induction was mediated through TLR9. We have previously shown that HHV-6B promotes Th1 responses and blocks Th2 responses in both humans and mice. We now show that neutralization of IFN-alpha but not IFN-lambda1 blocked the HHV-6B-induced enhancement of Th1 responses in MLR, but did not affect the HHV-6-induced dampening of Th2 responses. Similarly, blockage of TLR9 counteracted HHV-6Bs effects on the Th1/Th2 balance. In addition, IFN-alpha but not IFN-lambda1 promoted IFN-gamma production and blocked IL-5 and IL-13 production in purified CD4+ T-cells. The lack of effect of IFN-lambda1 correlated with the absence of the IFN-lambda receptor IL-28Ralfa chain on the cell surface of both resting and activated CD4+ T-cells. We conclude that inactivated HHV-6B is a strong inducer of IFN-lambda1 in plasmacytoid DC and that this induction is TLR9-dependent. However, human CD4+ T-cells do not express the IFN-lambda receptor and are refractory to IFN-lambda1 treatment. The HHV-6B-induced alterations in the Th1/Th2 balance are instead mediated mainly through TLR9 and IFN-alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human interferon lambda-1 (IFN-lambda1/IL-29) modulates the Th1/Th2 response.Genes Immun. 2007 Apr;8(3):254-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6364382. Epub 2007 Mar 15. Genes Immun. 2007. PMID: 17361203
-
IL-4 enhances IFN-lambda1 (IL-29) production by plasmacytoid DCs via monocyte secretion of IL-1Ra.Blood. 2010 May 27;115(21):4185-90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-246157. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20233967
-
Interferon-lambda1 (interleukin-29) preferentially down-regulates interleukin-13 over other T helper type 2 cytokine responses in vitro.Immunology. 2008 Dec;125(4):492-502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02862.x. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 18547367 Free PMC article.
-
Type III IFNs are produced by and stimulate human plasmacytoid dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2012 Sep 15;189(6):2735-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102038. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22891284 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular immunological approaches to biotherapy of human cancers--a review, hypothesis and implications.Anticancer Res. 2006 Mar-Apr;26(2A):1113-34. Anticancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16619514 Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphoproliferative Syndromes Associated with Human Herpesvirus-6A and Human Herpesvirus-6B.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018 May 1;10(1):e2018035. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2018.035. eCollection 2018. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29755712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory effects on dendritic cells by human herpesvirus 6.Front Microbiol. 2015 Apr 30;6:388. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00388. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25983728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon lambda in respiratory viral infection: immunomodulatory functions and antiviral effects in epithelium.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 1;15:1338096. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1338096. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38495892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-λs: special immunomodulatory agents and potential therapeutic targets.J Innate Immun. 2013;5(3):209-18. doi: 10.1159/000345365. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 23207147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human herpesvirus 6A infection in CD46 transgenic mice: viral persistence in the brain and increased production of proinflammatory chemokines via Toll-like receptor 9.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5421-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03763-13. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24574405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, Lewis-Antes A, Shen M, et al. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:69–77. - PubMed
-
- Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, Henderson K, Schlutsmeyer S, et al. IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:63–68. - PubMed
-
- Dumoutier L, Tounsi A, Michiels T, Sommereyns C, Kotenko SV, et al. Role of the interleukin (IL)-28 receptor tyrosine residues for antiviral and antiproliferative activity of IL-29/interferon-lambda 1: similarities with type I interferon signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:32269–32274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

