TIMP-1 induces an EMT-like phenotypic conversion in MDCK cells independent of its MMP-inhibitory domain
- PMID: 22701711
- PMCID: PMC3372473
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038773
TIMP-1 induces an EMT-like phenotypic conversion in MDCK cells independent of its MMP-inhibitory domain
Abstract
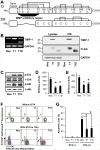
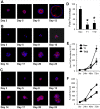
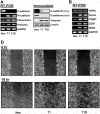
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their endogenous inhibitors (TIMPs) regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) critical for the development of epithelial organs as well as cancer cell invasion. TIMP-1 is frequently overexpressed in several types of human cancers and serves as a prognostic marker. The present study investigates the roles of TIMP-1 on the EMT process and formation of the lumen-like structure in a 3D Matrigel culture of MDCK cells. We show that TIMP-1 overexpression effectively prevents cell polarization and acinar-like structure formation. TIMP-1 induces expression of the developmental EMT transcription factors such as SLUG, TWIST, ZEB1 and ZEB2, leading to downregulation of epithelial marker and upregulation of mesenchymal markers. Importantly, TIMP-1's ability to induce the EMT-like process is independent of its MMP-inhibitory domain. To our surprise, TIMP-1 induces migratory and invasive properties in MDCK cells. Here, we present a novel finding that TIMP-1 signaling upregulates MT1-MMP and MMP-2 expression, and potentiates MT1-MMP activation of pro-MMP-2, contributing to tumor cell invasion. In spite of the fact that TIMP-1, as opposed to TIMP-2, does not interact with and inhibit MT1-MMP, TIMP-1 may act as a key regulator of MT1-MMP/MMP-2 axis. Collectively, our findings suggest a model in which TIMP-1 functions as a signaling molecule and also as an endogenous inhibitor of MMPs. This concept represents a paradigm shift in the current view of TIMP-1/MT1-MMP interactions and functions during cancer development/progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Vainio S, Muller U. Inductive tissue interactions, cell signaling, and the control of kidney organogenesis. Cell. 1997;90:978. - PubMed
-
- Gumbiner BM. Epithelial morphogenesis. Cell. 1992;69:387. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:454. - PubMed
-
- Leighton J, Estes LW, Mansukhani S, Brada Z. A cell line derived from normal dog kidney (MDCK) exhibiting qualities of papillary adenocarcinoma and of renal tubular epithelium. Cancer. 1970;26:1028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

