Metabolomic profiling reveals mitochondrial-derived lipid biomarkers that drive obesity-associated inflammation
- PMID: 22701716
- PMCID: PMC3373493
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038812
Metabolomic profiling reveals mitochondrial-derived lipid biomarkers that drive obesity-associated inflammation
Abstract
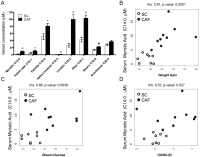
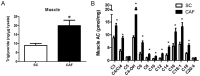
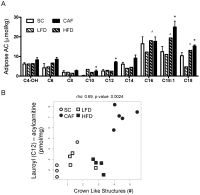
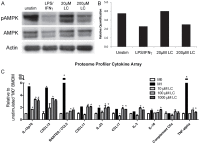
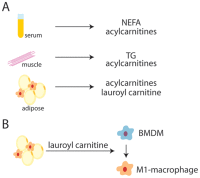
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions worldwide. Several animal models of obesity exist, but studies are lacking that compare traditional lard-based high fat diets (HFD) to "Cafeteria diets" (CAF) consisting of nutrient poor human junk food. Our previous work demonstrated the rapid and severe obesogenic and inflammatory consequences of CAF compared to HFD including rapid weight gain, markers of Metabolic Syndrome, multi-tissue lipid accumulation, and dramatic inflammation. To identify potential mediators of CAF-induced obesity and Metabolic Syndrome, we used metabolomic analysis to profile serum, muscle, and white adipose from rats fed CAF, HFD, or standard control diets. Principle component analysis identified elevations in clusters of fatty acids and acylcarnitines. These increases in metabolites were associated with systemic mitochondrial dysfunction that paralleled weight gain, physiologic measures of Metabolic Syndrome, and tissue inflammation in CAF-fed rats. Spearman pairwise correlations between metabolites, physiologic, and histologic findings revealed strong correlations between elevated markers of inflammation in CAF-fed animals, measured as crown like structures in adipose, and specifically the pro-inflammatory saturated fatty acids and oxidation intermediates laurate and lauroyl carnitine. Treatment of bone marrow-derived macrophages with lauroyl carnitine polarized macrophages towards the M1 pro-inflammatory phenotype through downregulation of AMPK and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Results presented herein demonstrate that compared to a traditional HFD model, the CAF diet provides a robust model for diet-induced human obesity, which models Metabolic Syndrome-related mitochondrial dysfunction in serum, muscle, and adipose, along with pro-inflammatory metabolite alterations. These data also suggest that modifying the availability or metabolism of saturated fatty acids may limit the inflammation associated with obesity leading to Metabolic Syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:579–591. - PubMed
-
- Lumeng CN, Maillard I, Saltiel AR. T-ing up inflammation in fat. Nat Med. 2009;15:846–847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 AA017376/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK034987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AA017376/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES019472/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK058398/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AA017376/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01DK58398/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 ES019472/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

