Ca2+ regulates the Drosophila Stoned-A and Stoned-B proteins interaction with the C2B domain of Synaptotagmin-1
- PMID: 22701718
- PMCID: PMC3373503
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038822
Ca2+ regulates the Drosophila Stoned-A and Stoned-B proteins interaction with the C2B domain of Synaptotagmin-1
Abstract
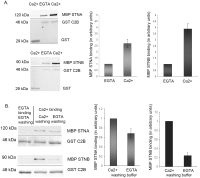
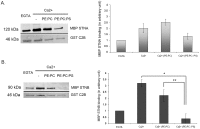
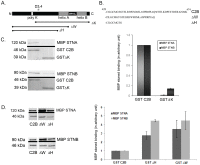
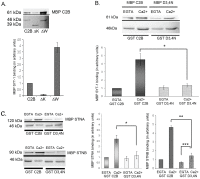
The dicistronic Drosophila stoned gene is involved in exocytosis and/or endocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Mutations in either stonedA or stonedB cause a severe disruption of neurotransmission in fruit flies. Previous studies have shown that the coiled-coil domain of the Stoned-A and the µ-homology domain of the Stoned-B protein can interact with the C2B domain of Synaptotagmin-1. However, very little is known about the mechanism of interaction between the Stoned proteins and the C2B domain of Synaptotagmin-1. Here we report that these interactions are increased in the presence of Ca(2+). The Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between the µ-homology domain of Stoned-B and C2B domain of Synaptotagmin-1 is affected by phospholipids. The C-terminal region of the C2B domain, including the tryptophan-containing motif, and the Ca(2+) binding loop region that modulate the Ca(2+)-dependent oligomerization, regulates the binding of the Stoned-A and Stoned-B proteins to the C2B domain. Stoned-B, but not Stoned-A, interacts with the Ca(2+)-binding loop region of C2B domain. The results indicate that Ca(2+)-induced self-association of the C2B domain regulates the binding of both Stoned-A and Stoned-B proteins to Synaptotagmin-1. The Stoned proteins may regulate sustainable neurotransmission in vivo by binding to Ca(2+)-bound Synaptotagmin-1 associated synaptic vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The products of the Drosophila stoned locus interact with synaptic vesicles via synaptotagmin.J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 15;20(22):8254-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08254.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11069931 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of stoned and synaptotagmin in synaptic vesicle endocytosis.J Neurosci. 2001 Feb 15;21(4):1218-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01218.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160392 Free PMC article.
-
Functional dissection of a eukaryotic dicistronic gene: transgenic stonedB, but not stonedA, restores normal synaptic properties to Drosophila stoned mutants.Genetics. 2003 Sep;165(1):185-96. doi: 10.1093/genetics/165.1.185. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 14504226 Free PMC article.
-
Role of synaptotagmin, a Ca2+ and inositol polyphosphate binding protein, in neurotransmitter release and neurite outgrowth.Chem Phys Lipids. 1999 Apr;98(1-2):59-67. doi: 10.1016/s0009-3084(99)00018-3. Chem Phys Lipids. 1999. PMID: 10358928 Review.
-
Stoned.Traffic. 2010 Jan;11(1):16-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00999.x. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 19883395 Review.
Cited by
-
The Genetic Basis of Natural Variation in Drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae) Virgin Egg Retention.J Insect Sci. 2017 Jan 27;17(1):5. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iew094. Print 2017 Jan. J Insect Sci. 2017. PMID: 28042107 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Drosophila Synaptotagmins in membrane trafficking at synapses.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 May;78(9):4335-4364. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03788-9. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33619613 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Littleton JT, Stern M, Schulze K, Perin M, Bellen HJ. Mutational analysis of Drosophila Synaptotagmin demonstrates its essential role in Ca2+-activated neurotransmitter release Cell. 1993;74:1125–1134. - PubMed
-
- Nonet ML, Grundahl K, Meyer BJ, Rand JB. Synaptic function is impaired but not eliminated in C. elegans mutants lacking synaptotagmin. Cell. 1993;73:1291–1305. - PubMed
-
- DiAntonio A, Schwarz TL. The effect on synaptic physiology of synaptotagmin mutations in Drosophila. Neuron. 1994;12:909–920. - PubMed
-
- Geppert M, Goda Y, Hammer RE, Li C, Rosahl TW, et al. Synaptotagmin 1: a major Ca2+ sensor for transmitter release at a central synapse. Cell. 1994;79:717–727. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

