Neuroglobin-overexpression reduces traumatic brain lesion size in mice
- PMID: 22703519
- PMCID: PMC3444402
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-67
Neuroglobin-overexpression reduces traumatic brain lesion size in mice
Abstract
Background: Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that over-expression of Neuroglobin (Ngb) is neuroprotective against hypoxic/ischemic brain injuries. In this study we tested the neuroprotective effects of Ngb over-expression against traumatic brain injury (TBI) in mice.
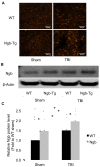
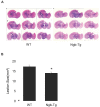
Results: Both Ngb over-expression transgenic (Ngb-Tg) and wild-type (WT) control mice were subjected to TBI induced by a controlled cortical impact (CCI) device. TBI significantly increased Ngb expression in the brains of both WT and Ngb-Tg mice, but Ngb-Tg mice had significantly higher Ngb protein levels at the pre-injury baseline and post-TBI. Production of oxidative tissue damage biomarker 3NT in the brain was significantly reduced in Ngb-Tg mice compared to WT controls at 6 hours after TBI. The traumatic brain lesion volume was significantly reduced in Ngb Tg mice compared to WT mice at 3 weeks after TBI; however, there were no significant differences in the recovery of sensorimotor and spatial memory functional deficits between Ngb-Tg and WT control mice for up to 3 weeks after TBI.
Conclusion: Ngb over-expression reduced traumatic lesion volume, which might partially be achieved by decreasing oxidative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Burmester T, Hankeln T. Neuroglobin: a respiratory protein of the nervous system. News Physiol Sci. 2004;19:110–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

